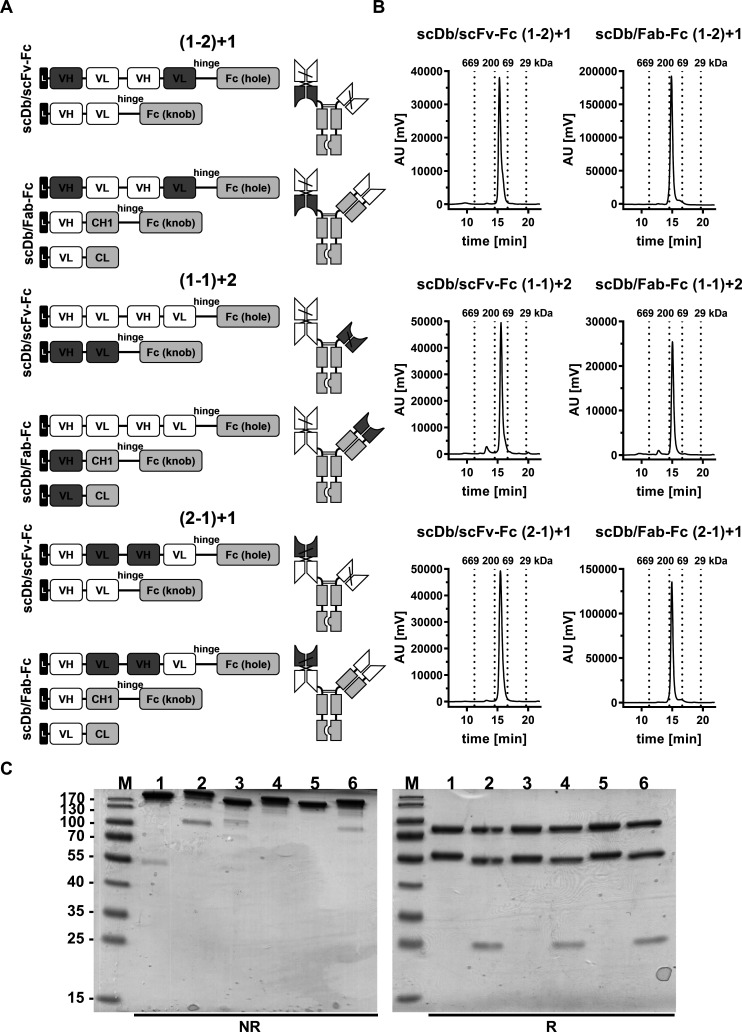
Figure 1.
Biochemical characterization of scDb/scFv-Fc and scDb/Fab-Fc variants. (A) Composition and schematic illustration of trivalent, bispecific antibodies. Nomenclature: 1 refers to the HER3 binding site, 2 refers to the CD3 binding site. Numbers in brackets refer to the binding sites of the scDb moiety. Variable domains of HER3 and CD3 are shown in white and dark gray, respectively. Constant domains are shown in light gray. (B) Size-exclusion chromatography by high performance liquid chromatography using a Tosoh TSKgel SuperSW mAb HR column. (C) Sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoreses analysis (12% PAA, 2 µg/lane, Coomassie blue staining) of (1) scDb/scFv-Fc (1-2)+1, (2) scDb/Fab-Fc (1-2)+1, (3) scDb/scFv-Fc (1-1)+2, (4) scDb/Fab-Fc (1-1)+2, (5) scDb/scFv-Fc (2-1)+1 and (6) scDb/Fab-Fc (2-1)+1 under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) condition. M, protein marker; AU, arbitrary units; CH1, constant heavy chain domain 1; CL, constant light chain domain; Fc, fragment crystallizable; scDb, single-chain diabody; VH, variable heavy chain domain; VL, variable light chain domain,