Figure 1:
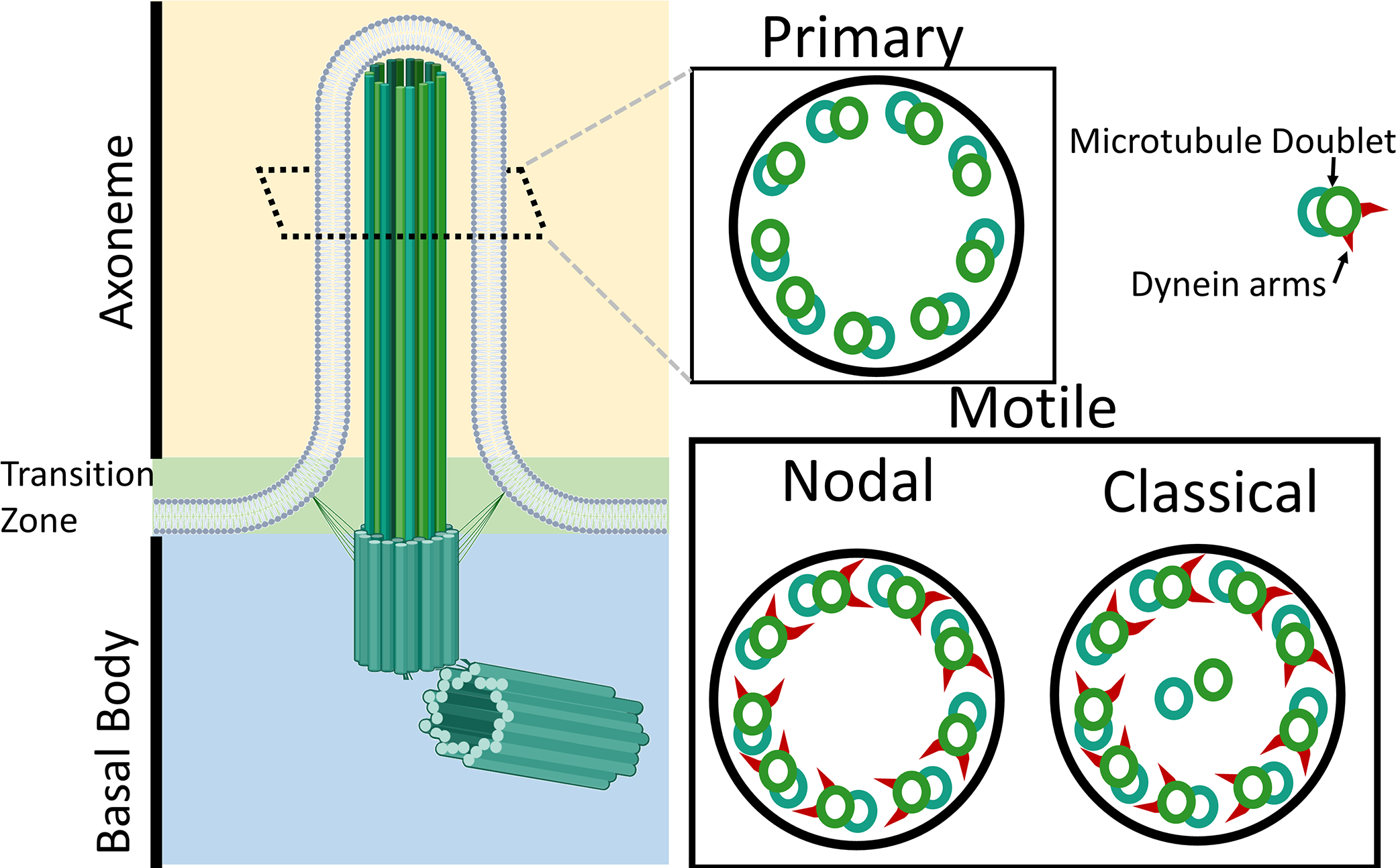
Structure of cilia. The cilia are composed of three main sections, the axoneme which performs the sensory or movement function, the transition zone which likely contains over 100 proteins which function to anchor the cilia and regulate transport to and from the cilia, and the basal body which is a centriole that functions as a tubulin organizing center to form the cilia. Diagram showing the cross section of the axoneme of common types of motile and primary cilia in vertebrates.
