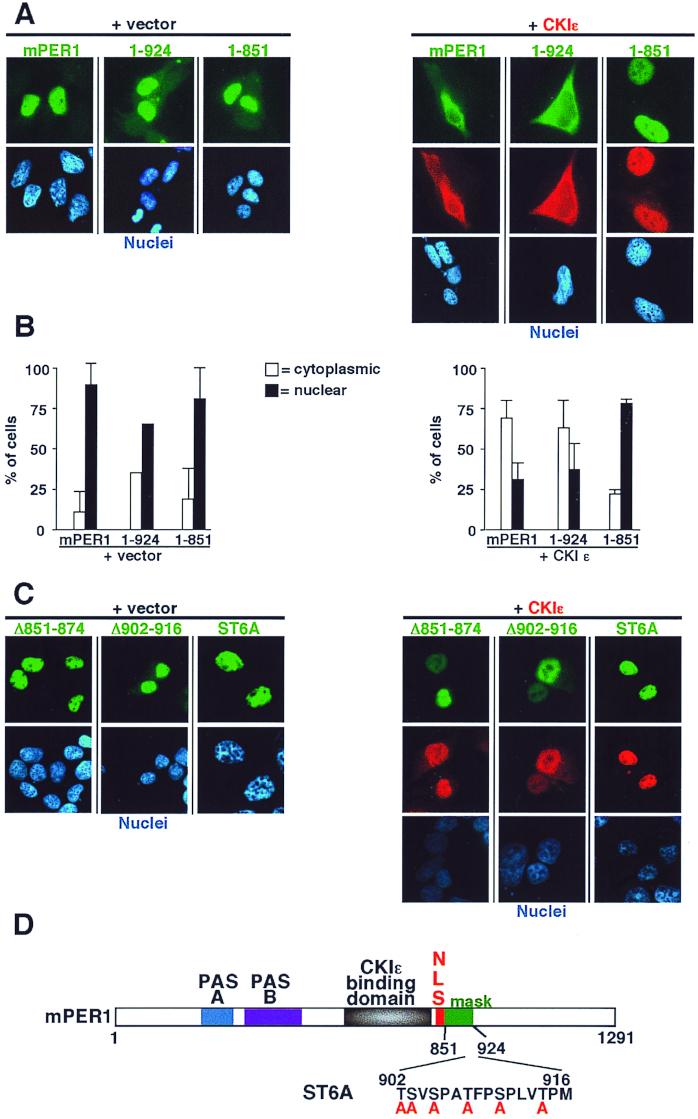
FIG. 7.
CKIɛ-mediated cytoplasmic retention of mPER1 requires a masking domain (amino acids 851-924). (A) Full-length (mPER1) and amino-terminal fragments (1-924 and 1-851) of Myc-mPER1 were expressed in HEK 293 cells without (left) or with (right) HA-CKIɛ. Forty-eight hours posttransfection, the localization of mPER1 and CKIɛ was assessed as described above. The mPER1(1-851) construct contains an NLS and can bind to CKIɛ but failed to relocalize to the cytoplasm. Full-length and mPER1(1-924) were retained in the cytoplasm by coexpression of CKIɛ. Representative micrographs are shown. (B) Quantitation of the experiments shown in panel A. (C) Internal deletions and mutation of potential phosphorylation sites disrupts the function of the masking domain. HEK 293 cells were transfected as above with Myc-mPER1 containing deletion of residues 851 to 874 (Δ851-874) or 902 to 916 (Δ902-916) or with simultaneous mutations of six serine and threonine residues between amino acids 902 to 916 region (ST6A). None of the mutations altered nuclear localization, while all abrogated the ability of CKIɛ to relocalize Myc-mPER1 to the cytoplasm. (D) Cartoon of mPER1 with identification of masking domain and mutant ST6A.