Fig. 3. The secretion of Cit-Vim is dependent on the activation of Akt1 and PAD2, and citrullinated arginine (R) is identified by IP-MS.
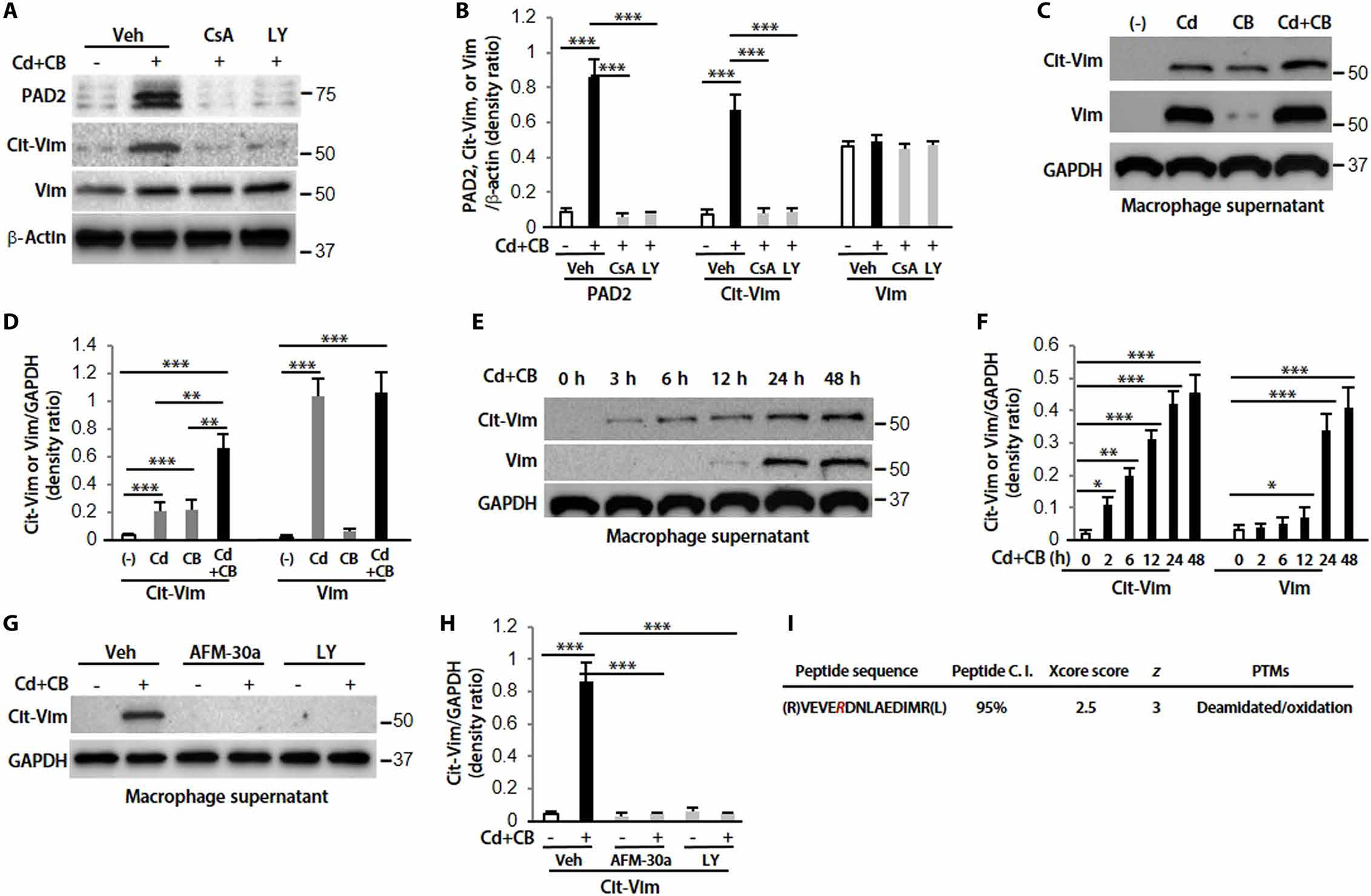
(A) Immunoblot analysis in lung macrophages treated with Sal or CdCl2 (1.8 μg/ml) plus CB (10 μg/ml) for 2 hours. Cells were pretreated with vehicle (Veh), CsA (20 μM), or LY (20 μM) for 2 hours. (B) Quantification of PAD2, Cit-Vim, and Vim expression from (A) (n = 3). (C) Supernatants were concentrated and analyzed by immunoblot analysis at 48 hours. (D) Quantification of Cit-Vim and Vim expression from (C) (n = 3). (E) Different time points by CdCl2 plus CB. (F) Quantification of Cit-Vim and Vim expression from (E) (n = 3). (G) Pretreatment with AFM-30a (5 μM) overnight or LY for 2 hours, followed by CdCl2 plus CB for 48 hours. (H) Quantification of Cit-Vim expression from (G) (n = 3). (I) Immunoprecipitated samples were performed with MS analysis for the citrullinated cites. The deamination (also termed citrullination) site was indicated by R (as highlighted in magenta; the residue number is AA175 based on the UniProtKB sequence). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis.
