Fig. 8. Cd/CB-induced interstitial fibrosis in mice is TLR4 dependent.
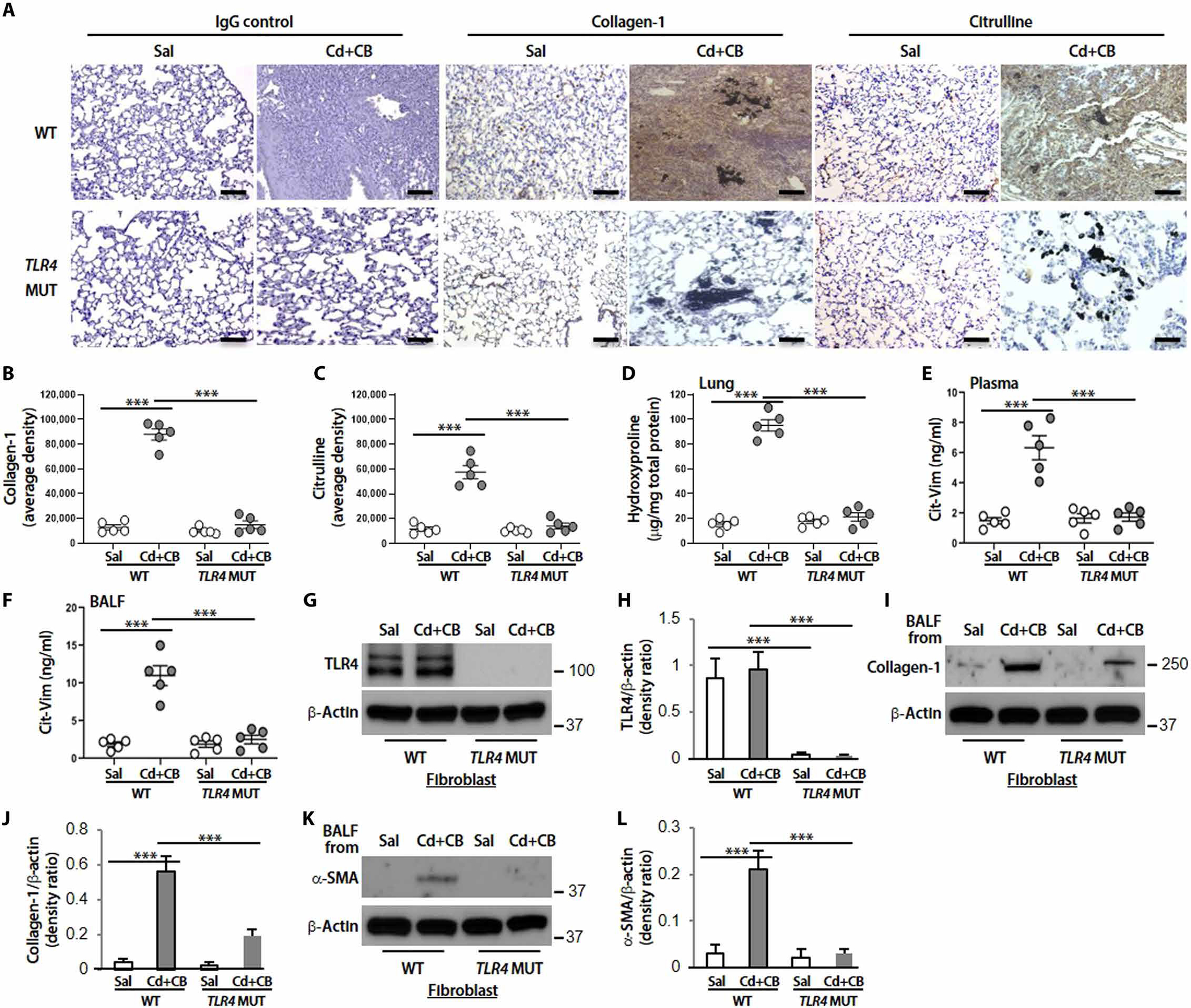
TLR4 WT or TLR4 MUT mice (n = 5 per group) were treated intratracheally with Sal or CdCl2 + CB (CdCl2, 0.16 mg/kg; CB, 5.0 mg/kg). (A) Representative lung histology with collagen-1 and citrulline staining at day 14. DAB staining densities from (A) for (B) collagen-1 and (C) citrulline were quantified. Scale bars, 100 μm. (D) Hydroxyproline content at day 14. Cit-Vim amounts by ELISA in (E) plasma and (F) BALF at day 14 after mice exposure. (G) Immunoblot analysis of TLR4. (H) Quantification of TLR4 expression from (G) (n = 3). (I) Collagen-1. (J) Quantification of collagen-1 expression from (I) (n = 3). (K) α-SMA. (L) Quantification of α-SMA expression from (K) (n = 3) in lung fibroblasts isolated from TLR4 WT or TLR4 MUT mice. For checking collagen-1 and α-SMA expression, cells were cultured with BALF collected from Sal- or CdCl2 + CB–treated mice. Each dot represents individual mouse. ***P < 0.001 using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis.
