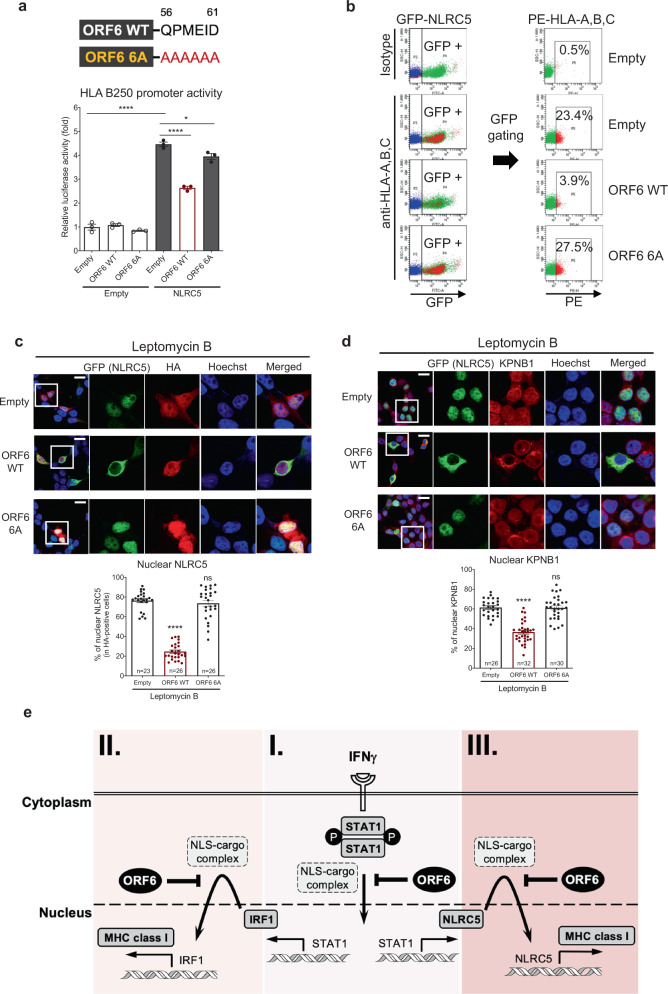
Fig. 7. The carboxy-terminus region of SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 is required for inhibition of the NLRC5 function.
a Role of the carboxy-terminus region of SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 on NLRC5-mediated HLA-B promoter activity. The schematic image of SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 shows the position of the mutated amino acid at ORF6 C' terminus end. HEK293T cells were transfected with HLA-B promoter-containing reporter construct and plasmids expressing empty or NLRC5, along with plasmids expressing empty, WT, or 6 A mutant of ORF6. At 36 h after transfection, cells were collected to measure the luciferase activity. The results are from three independent experiments. b Effect of SARS-CoV-2 WT or 6 A mutant ORF6 on NLRC5-mediated surface expression of HLA-A, B, and C proteins analyzed by flow cytometry. GFP (NLRC5) positive cells were gated for evaluating the PE (HLAs) signal intensity (%). The FACS gating strategies are provided in Supplementary Fig. 12. c and d Immunofluorescence analysis of the cellular localization of GFP-tagged NLRC5 (c) or endogenous KPNB1 (d) by HA alone, HA-tagged SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 WT, or 6A mutant. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing the indicated proteins. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were treated with 100 nM of Leptomycin B for 8 h, and then analyzed by confocal microscopy. Quantitative comparison of the nuclear signal intensity (% of nuclear signal intensity/total cell signal intensity) of NLRC5 or KPNB1 is shown with a bar graph using ImageJ. The scale bar indicates 20 mm. The sample numbers for evaluation are indicated in the bar graph. e The type II IFN system is a master host immune response for the MHC class I-mediated antigen-presenting pathway upon invasion by intracellular pathogens or cancer. I Activation of IFNGR by IFNγ triggers immediate phosphorylation of STAT1. Subsequently, phosphorylated STAT1 undergoes homodimerization, and the dimerized STAT1 complex can translocate to the nucleus. Nuclear-localized STAT1 initiates its function as a transcription factor for the expression of the IFNγ-inducible genes, including IRF1 and NLRC5. Upon production, IRF1 (II) and NLRC5 (III) translocate to the nucleus and function as transcription factors for induction of the MHC class I pathway. All three transcriptional regulators possess NLS and utilize the karyopherin-associated import complex for entering the nucleus. However, SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 targets this nuclear translocation by blocking karyopherin-mediated protein import of these MHC class I-activating transcription factors, thereby resulting in suppressed MHC class I expression upon viral infection.