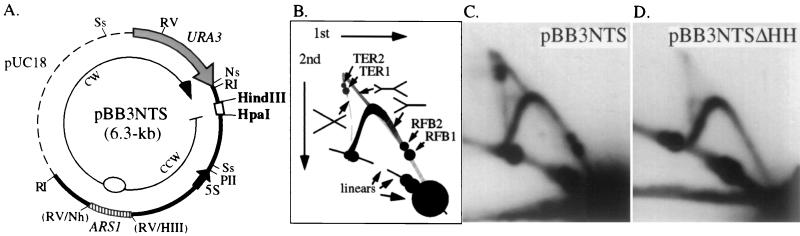
FIG. 3.
Deletion of the HindIII-HpaI region eliminates RFB1 and RFB2. (A) Map of the 6.3-kb plasmid pBB3NTS. The dashed line is vector sequence from pUC18. Only relevant restriction sites are noted. The thicker line between the EcoRI (RI) sites corresponds to the 2.46-kb EcoRI NTS region (a subfragment from the restriction map in Fig. 1) from the rDNA of RM14-3a. The locations of ARS1 and URA3 are indicated. A 425-bp NheI-HindIII (Nh-H3) fragment containing ARS1 was blunt-ended and inserted into the EcoRV (RV) site near the rDNA ARS (Fig. 1) to improve the efficiency of extrachromosomal maintenance of the plasmid. Bidirectional replication initiating from ARS1 creates a CCW fork that is blocked by the RFBs before meeting the CW fork. Ss, SspI; Ns, NsiI; Sp, SphI; PII, PvuII. (B) Schematic diagram of the migration of different replication intermediates in 2D gels shown in C and D. Accumulation of arrested forks results in the two intense spots of hybridization (RFB1 and RFB2) along the arc of Y intermediates. The nearly vertical dashed line represents the pattern of hybridization seen for X-shaped, or terminating, molecules. Termination at RFB1 and RFB2 results in the accumulation of X-shaped molecules TER1 and TER2, respectively. The thicker diagonal gray line corresponds to the hybridization pattern for double-Y replication intermediates. (C and D) High-resolution 2D gels of the 2.2-kb SspI (Ss in panel A) fragment from pBB3NTS and pBB3NTSΔHH, respectively, probed with URA3 sequences.