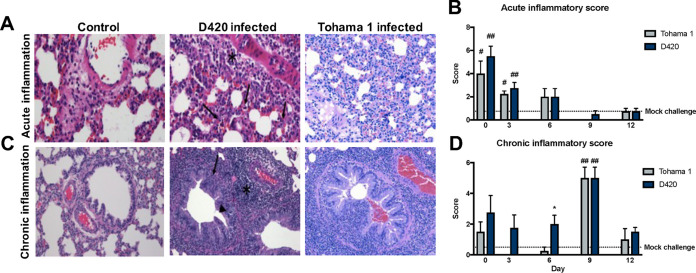
FIG 4.
B. pertussis infection induces acute and chronic inflammation in the lungs of Sprague-Dawley rats. The left lobe of the lung was sectioned and stained with H&E from rats infected with D420 or Tohama 1 or from the PBS control. (A) Representative images of acute inflammation demonstrating neutrophil recruitment around surrounding blood vessel (asterisk) and parenchyma (arrows) at ×400 magnification. (B) Average acute inflammatory score of the lung based on the predominance of neutrophils in the parenchyma, blood vessels, and airways. (C) Representative images of chronic inflammation showing mononuclear cells surrounding the blood vessel (asterisk), lamina propria (arrow), and bronchioles (arrowhead) at ×200 magnification. (D) Average chronic inflammatory score of the lungs characterized by mononuclear infiltrates in the parenchyma, blood vessels, and airway. Histological assessment was determined blinded with no knowledge of the treatment groups. The results are shown as means ± the SEM (n = 4). P values were determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s comparison test (*, P < 0.05 [compared between challenge groups]; #, P < 0.05, ##, P < 0.01 [compared to mock challenge]).