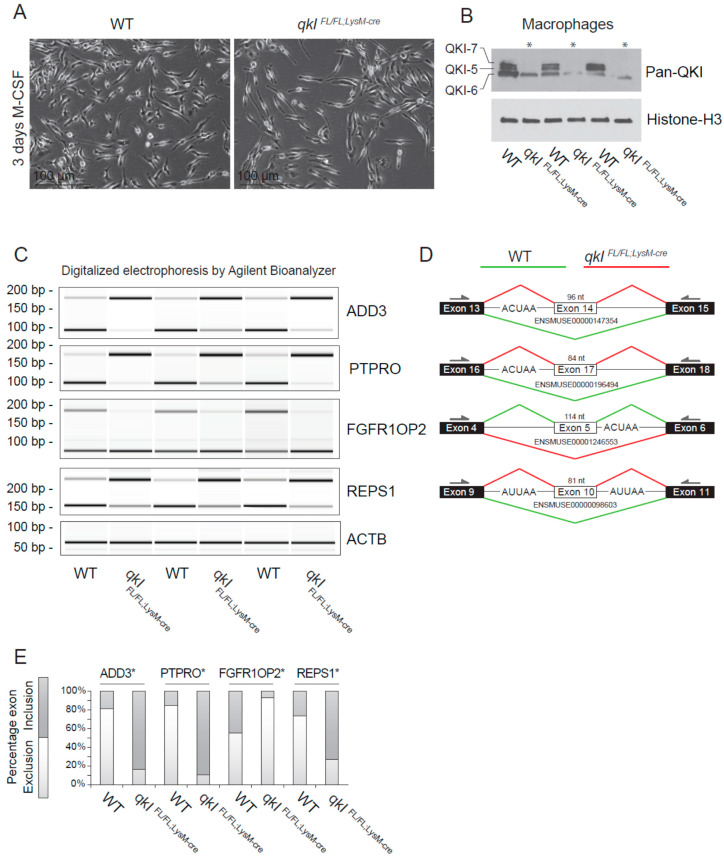
Figure 4.
QKI mediates alternative splicing in macrophages. (A) Photomicrographs of cultured bone marrow-derived macrophages 3 days after M-CSF stimulation. (B) Western blot analysis of cultured mouse macrophages from qkIFL/FL;LysM-cre or wild-type littermate controls using a pan-QKI (N-terminal) antibody and histone H3 loading control. (C) PCR analysis of cassette exon alternative splicing in 5 days M-CSF stimulated cultured macrophages derived from either wild-type or qkIFL/FL;LysM-cre mouse bone marrow. Gel electrophoresis of PCR products generated using primers in flanking exons are shown as digitalized electrophoresis by Agilent Bioanalyzer, illustrating the abundance of alternative mRNA isoforms expressed. (D) In silico analysis of the particular exon assessed illustrates the predicted alternative splicing event based on QRE position (defined as an ACUAA/AUUAA motif) and denotes the predominant splicing event in wild-type (green line) or qkIFL/FL;LysM-cre (red line) macrophages. * p ≤ 0.05 by Students’ t-test. (E) Densitometric quantification of bands in panel (C) using ImageJ software and statistical testing is provided for the assessed splicing events.