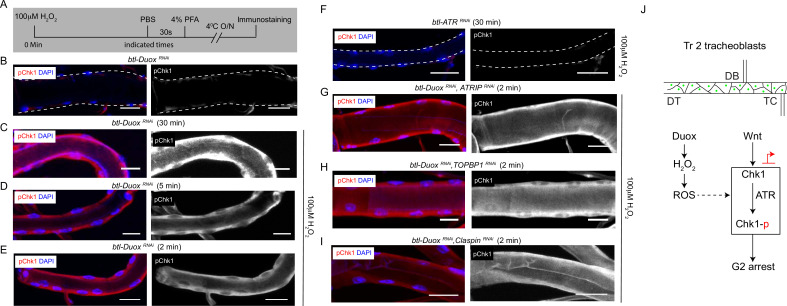
Figure 5. Incubation with H2O2 can restore phosphorylated checkpoint kinase 1 (pChk1) levels in Dual oxidase (Duox)-deficient tracheoblasts.
(A–E) Kinetics of Chk1 phosphorylation upon exposure to H2O2 ex vivo. (A) Regimen for H2O2 treatment and analysis of pChk1 in Tr2 dorsal trunk (DT) in L2. pChk1 immunostaining (red) in Tr2 DT in (B) untreated btl-DuoxRNAi (btl-GAL4/+; UAS-DuoxRNAi (32903)/+)-expressing tracheae and treated with 100 µM H2O2 for (C) 30 min, (D) 5 min, and (E) 2 min. (F) Effect of knockdown of ATR on Chk1 activation in Tr2 DT upon exposure to H2O2 ex vivo. pChk1 immunostaining (red) in Tr2 DT in btl-ATRRNAi (btl-GAL4/UAS-ATRRNAi) tracheae treated with 100 µM H2O2 for 30 min. (G–I) Effect of knockdown of Duox and ATRIP or TOPBP1 or Claspin on pChk1 levels in Tr2 DT in tracheae exposed to 100 µM H2O2 at L2. pChk1 immunostaining (red) in Tr2 DT in (G) btl-DuoxRNAi, ATRIPRNAi (btl-GAL4/ UAS-ATRIPRNAi; UAS-DuoxRNAi (32903)/+), (H) btl-DuoxRNAi, TOPBP1RNAi (btl-GAL4/+; UAS-DuoxRNAi(32903)/UAS-TOPBP1RNAi) and (I) btl-DuoxRNAi, ClaspinRNAi (btl-GAL4/+; UAS-DuoxRNAi(32903)/UAS-ClaspinRNAi) tracheae treated with 100 µM H2O2 for 2 min at L2. (J) Model for the regulation of ATR/Chk1 activation in Tr2 DT. We propose that H2O2 can induce ATR-dependent phosphorylation and activation of Chk1 in the absence of detectable DNA damage, leading to G2 arrest in Tr2 tracheoblasts. Scale bars = 10 µm.