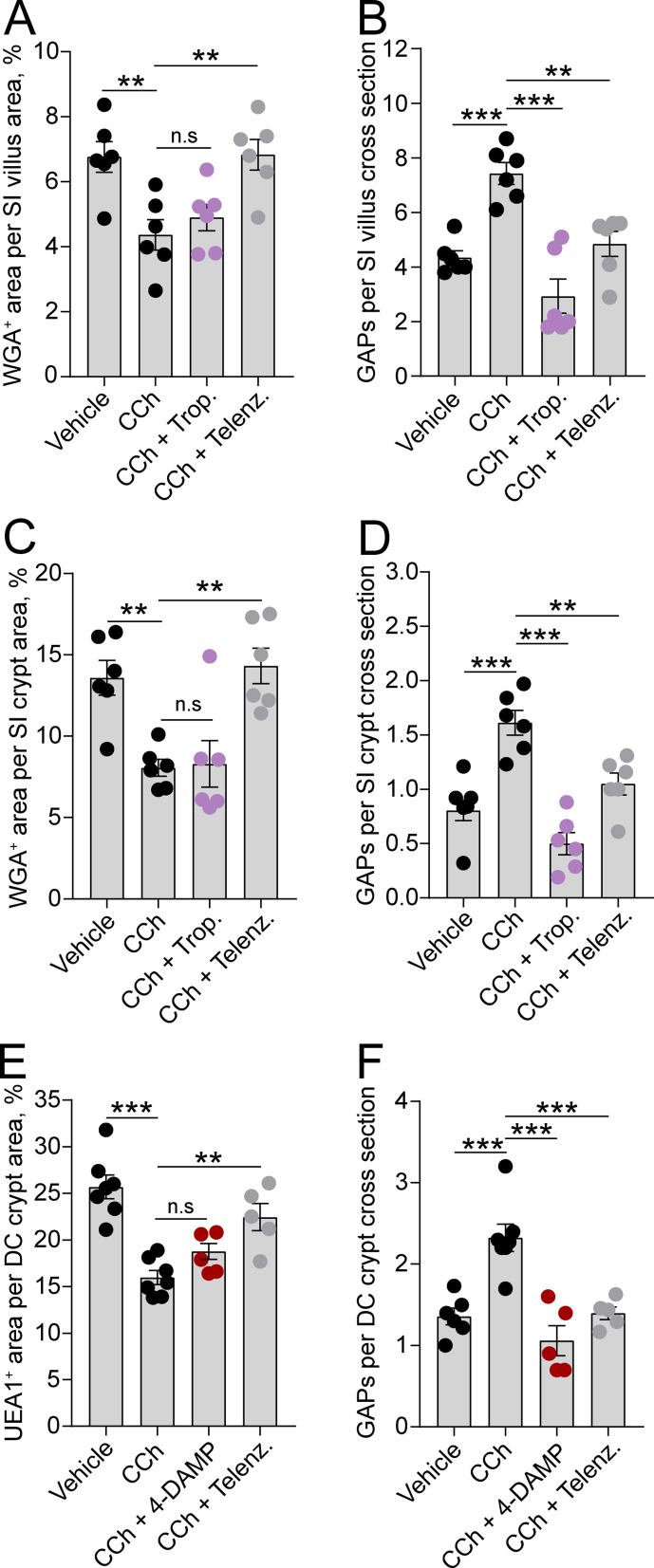
Figure 5. Carbamylcholine (CCh)-induced goblet cell-associated antigen passage (GAP) formation and mucus secretion use different muscarinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptors.
Effect of the muscarinic ACh receptor 4 (mAChR4) antagonist tropicamide (Trop.), the mAChR1 antagonist telenzepine (Telenz.), or the preferential mAChR3 antagonist 1,1-dimethyl-4-diphenylacetoxypiperidinium iodide (4-DAMP) on CCh-induced mucus secretion and GAP formation in the small intestine (SI) villus (A–B), the SI crypt (C–D), and the distal colon crypt (E–F). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n.s = non-significant, as compared to CCh. A–B, D–E, n = 6 in all groups. (C and F) Vehicle and CCh n = 7, CCh + 4 DAMP and CCh + Telenz. n = 5. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet’s post hoc test. Each data point represents the average of 25 villi or 40 crypts from one mouse.