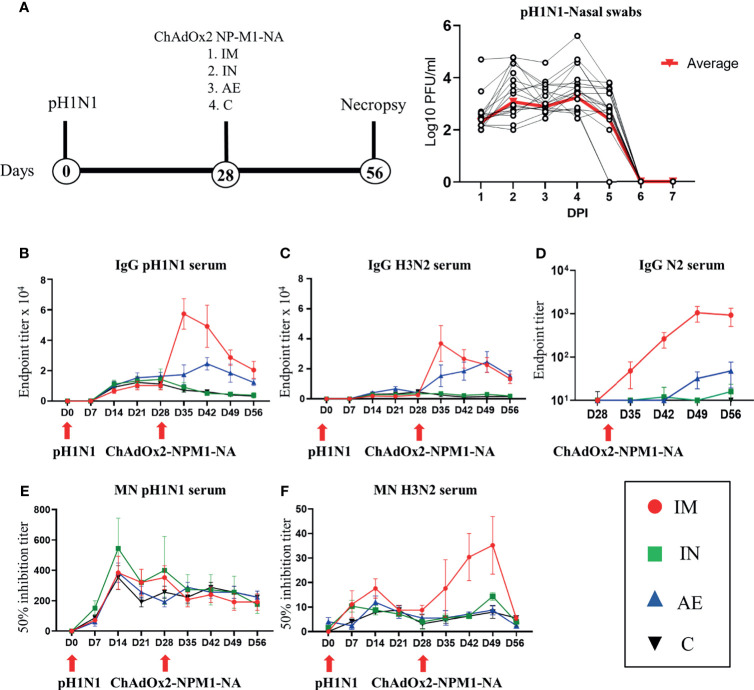
Figure 1.
Experimental design, viral load, and systemic antibody responses. (A) Twenty pigs were infected with pH1N1 influenza A virus and, 4 weeks later, immunized with ChAdOx2-NPM1-NA intramuscularly (IM), intranasally (IN), or by aerosol (AE). Four weeks later, they were culled. Weekly blood samples were collected during the time course. Control (C) animals were infected but not immunized. Virus load was determined by plaque assay of daily nasal swabs (NS) obtained at the indicated days post-infection (DPI). Each black line represents one animal. The thick red line indicates the mean of 20 animals. (B) pH1N1-, (C) H3N2-, and (D) N2-specific IgG responses in serum were determined by ELISA at the indicated time points. (E, F) Serum-neutralizing titers over time were determined by microneutralization (MN) of (E) pH1N1 and (F) H3N2 viruses. The mean and standard error (SEM) is presented in each time point. The arrows below D0 and D28 indicate challenge of the pigs with pH1N1 and immunization with ChAdOx2-NPM1-NA, respectively. Significant statistical differences are listed in Table 2 .