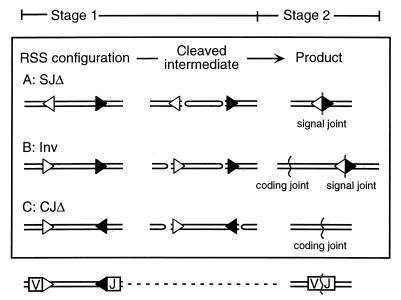
FIG. 1.
Configuration-specific differences in recombination outcome. RSS orientation dictates the type of junction that will be recovered after recombination. Three different outcomes, a signal joint via deletion, a signal and coding joint via inversion, and a coding joint via deletion via represent the recovered products resulting from the configurations shown in sections A, B, and C, respectively. Regardless of configuration, stage 1 operations involve cleavage at the heptamers of each RSS (shown as an open triangle for the 12-RSS and as a solid triangle for the 23-RSS). At the end of stage 1, as shown in the middle column (‘Cleaved intermediate’), two blunt signal ends and two hairpin-terminated coding ends are formed in every case. Subsequently, during stage 2, there are different operations required for resolution of the coding and/or signal ends. The identity of stage 1 operations and the divergence of stage 2 operations with different configurations forms the basis for distinguishing the postcleavage effects of RSS sequence in vivo.