Figure 1.
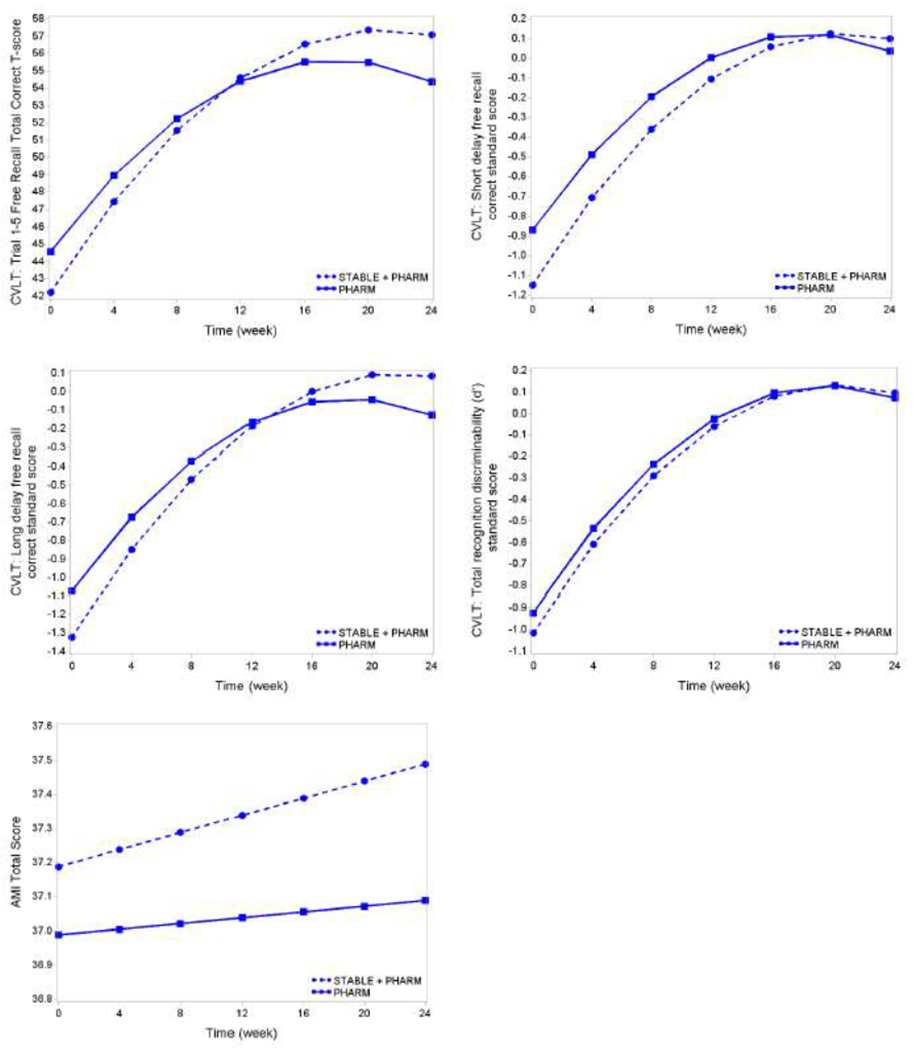
Trajectories of Memory Domain Neurocognitive Outcomes over the 6-month Study Period By Treatment Arm Using Model-Derived Adjusted Treatment Means
California Verbal Learning Test (CVLT) - anterograde verbal learning and memory:
These graphs show adjusted least squares means from quadratic mixed effects models with random intercept using unstructured covariance adjusted for site, psychosis, age, Wechsler Test of Adult Reading and Ham-D (time varying).The within group improvement from baseline was statistically significant at p≤0.05 for all CVLT items in both treatment groups (Item, p-value [DF, t-statistic]: Item12 Stable: <0.0001 [474, 9.67], Pharm: <0.0001 [479, 6.10]; Item16 Stable: <0.0001 [469, 8.55], Pharm: <0.0001 [475, 5.93]; Item20 Stable: <0.0001 [472, 9.31], Pharm: <0.0001 [478, 5.97]; Item44 Stable: <0.0001 [473, 7.01], Pharm: <0.0001 [480, 6.00]). There were no significant differences between the ECT plus Medication and Medication only treatment arms at the post-treatment (24 weeks) time point. For the comparison of trajectories of CVLT mean scores over time (time as continuous), there was a significant interaction for CVLT Trial 1–5 Free Recall Total Correct t-score (p [DF, t-statistic]: 0.02 [480, −2.27]) and CVLT Long delay free recall correct standard score (p [DF, t-statistic]: 0.04 [479, −2.11])
AMI-SF - retrograde amnesia for autobiographical information:
This graph shows adjusted least squares means from linear mixed effects model with random intercept using unstructured covariance adjusted for site, psychosis, age, Wechsler Test of Adult Reading and Ham-D (time varying). There was no significant differences between the ECT plus Medication and Medication only treatment arms at the post-treatment (24 weeks) time point. The within group improvement from baseline was not statistically significant in both treatment groups.
