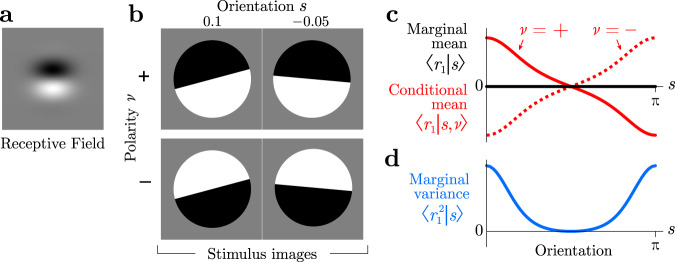
Fig. 1. Simple nonlinear code for orientation induced by two polarities.
a Receptive field for a linear neuron. b Four example images, each with an orientation s ∈ [0, π) and a polarity ν ∈ {−1, +1}. c The mean response of the linear neuron is tuned to orientation if polarity were specified (conditional mean, red). But when the polarity is unknown and could take either value, the mean response is untuned (marginal mean, black). d Tuning is recovered by the marginal variance even if the polarity is unknown (blue).