Figure 1.
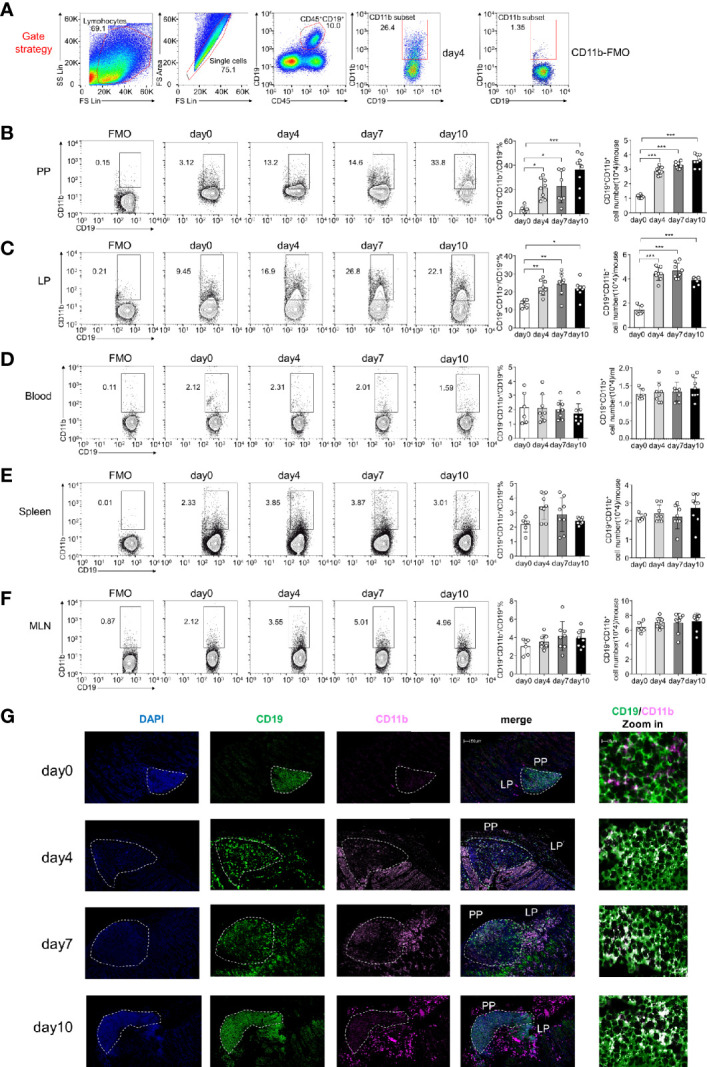
CD11b is induced in Peyer’s patches (PPs) and colorectal lamina propria (LP) B cells during dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. Flow cytometry was used to analyze the frequency and absolute number of CD11b+ B cells. (A) Gating strategy for the identification of CD19+CD11b+ cells in gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). Representative data from the LP of colitis mice on day 4 after DSS induction. Different fluorochrome-labeled isotype control antibodies or anti-CD45, -CD19, and -CD11b antibodies were used for staining. Numbers indicate the percentage of positive cells. The right panel represents CD11b fluorescence minus one (FMO) staining. Cells were isolated from the PPs (B), colorectal LP (C), total blood cell (D), spleen (E), and MLN (F) of DSS-induced WT mice on days 0, 4, 7, and 10. The absolute numbers were counting as follow: for PPs, colorectal LP, spleen, and MLN, the number of cells in that organ per mouse times the ratio of CD11b+B cells to obtain absolute count/mouse; for blood cell, 200ul blood cells were counted after red blood cell lysis, the number of 200ul blood cells times five and times the ratio of CD11b+B cells to obtain absolute count/ml. (G) Immunofluorescence of CD11b+CD19+ B cells in PPs and LPs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of one experiment with six to eight mice, performed in triplicate with similar results.
