Fig. 3. Peptide 1/miRNA-215 and Peptide 1/miRNA-206 nanoparticles attenuate the oncogenic signature of mesothelioma in vitro.
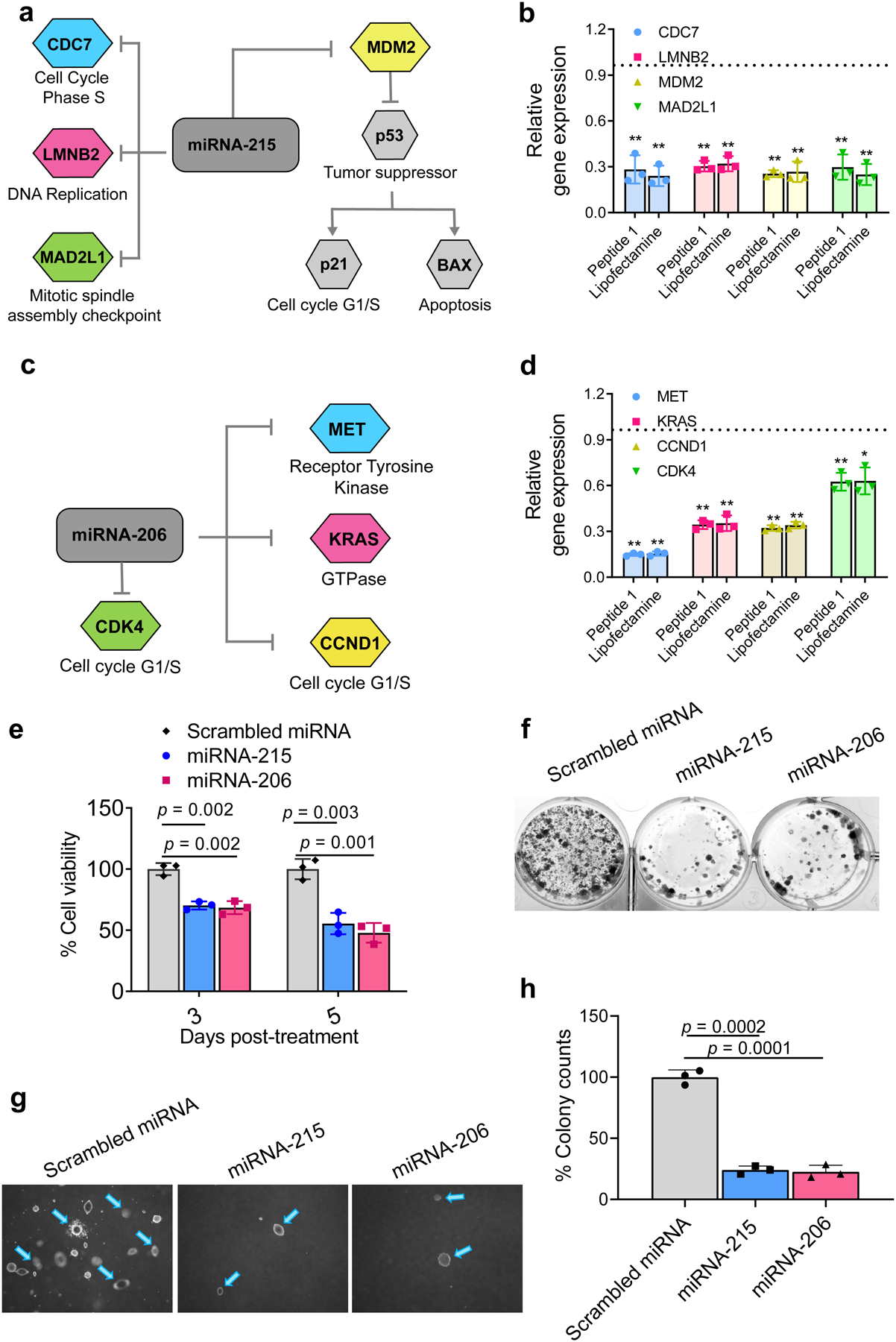
a, miRNA-215 silences key genes important to mesothelioma oncogenesis. b, miRNA-215 nanoparticles decrease expression levels of target genes relative to scrambled miRNA particles in H2052 cells 48 h post-treatment compared to Lipofectamine under similar conditions. Data = mean ± SD, n = 3 independent experiments, **p <0.01, two-tailed student’s t test. c, miRNA-206-targetted genes. d, miRNA-206 nanoparticles decrease expression levels of target genes relative to scrambled miRNA particles in H2052 cells 48 h post-treatment compared to Lipofectamine under similar conditions. Data = mean ± SD, 3 independent experiments, **p <0.01, *p <0.05, Significant difference was assessed by two-tailed student’s t test. e, H2052 cell viability at day 3 and 5 post-treatment with the nanoparticles delivering miRNA-215 and miRNA-206. Data = mean ± SD, n = 3 independent experiments, Significant difference was assessed by two-tailed student’s t test. f, Clonogenicity of H2052 cells treated with the nanoparticles delivering miRNA-215 and miRNA-206, 2 weeks post-treatment. Representative image is shown for n = 3 independent samples. g, Anchorage-independent 3D growth of cells 6 weeks after treatment with the nanoparticles delivering miRNA-215 and miRNA-206. h, Quantification of 3D colony formation, Data = mean ± SD, n = 3 independent samples. Significant difference was assessed by two-tailed student’s t test.
