Figure 6. Robust therapeutic effect of CMPCDA in multiple tumor models.
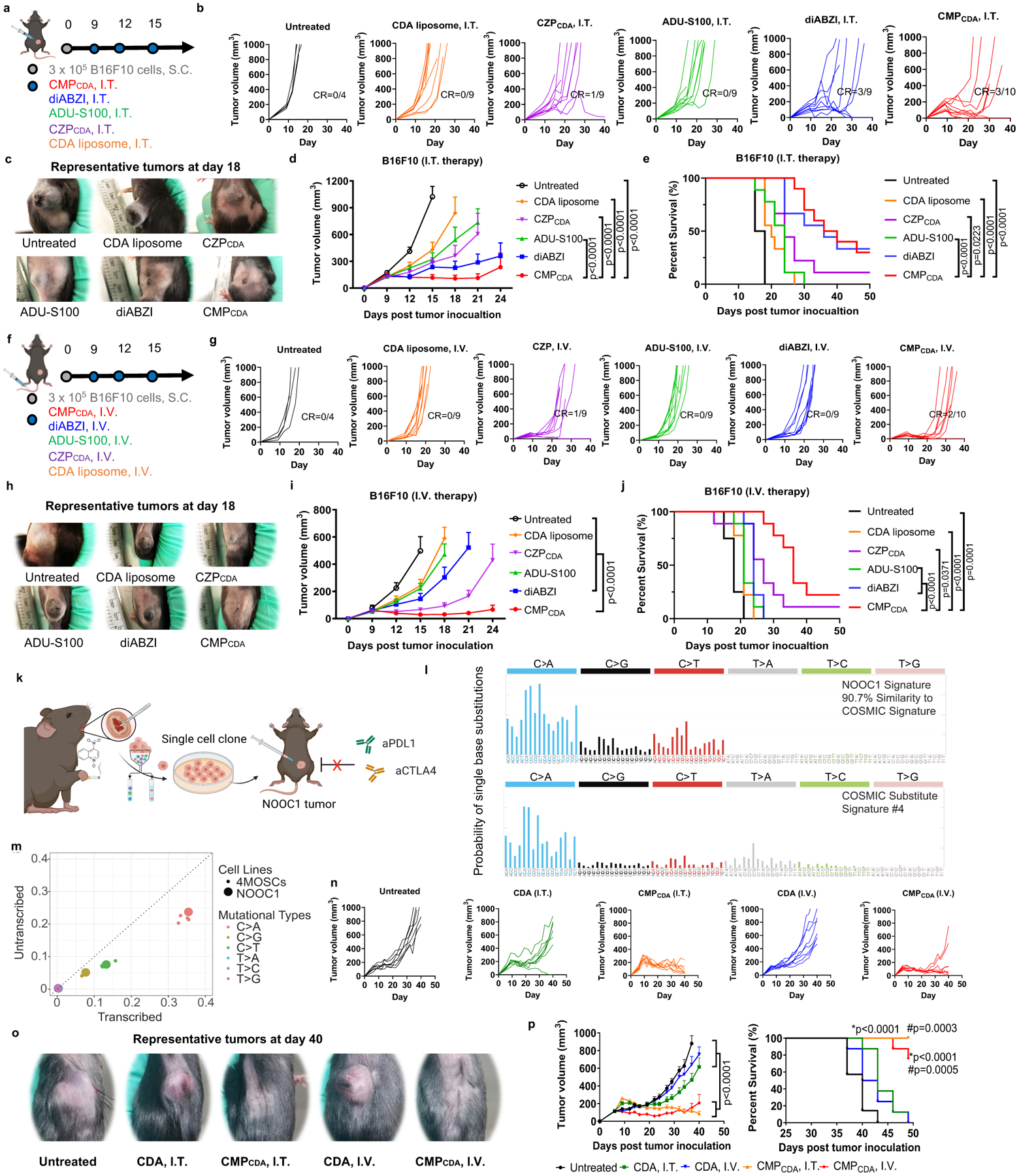
a–j) Therapeutic effect of CMPCDA was compared with other CDA formulations and other STING agonists in an established B16F10 tumor model. a–e) Tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice were treated with CMPCDA, CDA-Zn particle (CZPCDA), CDA liposome), ADU-S100, or diABZI (all 5 μg doses of STING agonists, I.T.) on the indicated time points (a). Shown are b) the individual tumor growth, c) representative photos of tumors, d) average tumor growth and e) survival. f–j) Tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice were treated with the indicated regimens (all 20 μg doses, I.V.) (f). Shown are g) the individual tumor growth, h) representative photos of tumors, i) average tumor growth, and j) survival. k–p) Therapeutic effect of CMPCDA in an immune checkpoint blocker (ICB)-resistant tobacco-associated tumor model (NOOC1). k) NOOC1 single-cell clone were isolated from the visible oral squamous cell carcinoma lesions of C57BL/6J mice treated with 4NQO-containing drinking water for 16 weeks. l) Mutational signatures indicate NOOC1 tumors with high fidelity to human cancers. m) Mutational profile of NOOC1 in comparison to other 4NQO-induced murine squamous cell carcinoma cell lines (4MOSCs). n–p) NOOC1 tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice were treated with CDA in CMPCDA or free form via I.T. (5 μg dose) or I.V. route (20 μg dose) on days 9, 12, 16, and 20 post tumor inoculation. Shown are n) the individual tumor growth, o) representative photos of tumors, p) average tumor growth and survival. Data represent mean ± SEM, from a representative experiment from 2 independent experiments with n = 4–10 (d–e, i–j) and n = 7–8 (n-p). Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA (d, i, p) with Bonferroni multiple comparisons post-test. Survival of (e, j, p) was analyzed by Kaplan–Meier survival analysis with log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. *p and #p in (p) denote statistical significance relative to the untreated and CDA groups, respectively. Figure 6a, 6fk, and 6k were created using BioRender.com.
