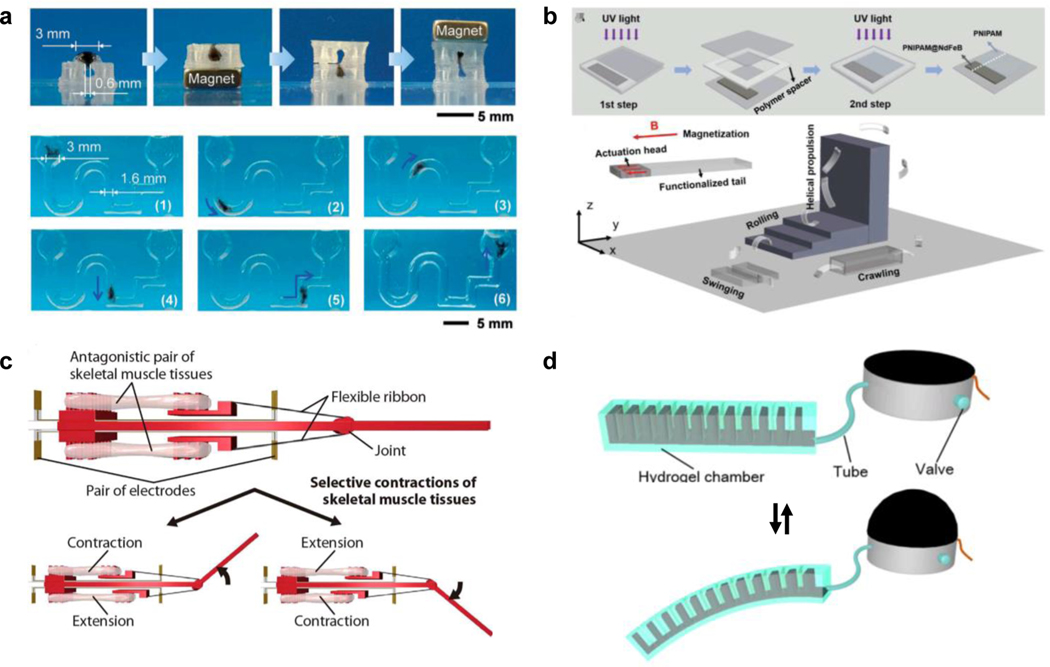
Figure 10. Robotic MAMs with different actuating mechanisms.
a) An example of a paramagnetic DNA hydrogel soft robot with magnetic field-driven navigation of its locomotion. Readapted with permission[116b]. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. b) A ferromagnetic hydrogel MAMs embedded with NdFeB particles. The MAM is pre-magnetized during fabrication to develop the ferromagnetic response, resulting in a more sophisticated moving behavior of the soft robot under a magnetic field. Readapted with permission[116c]. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. c) A bio-actuated MAM comprised of a muscle cell-laden Matrigel scaffold. Actuation of this MAM is activated by applying electrical stimulation with embedded gold electrodes, triggering contraction of the cells. Readapted with permission[116f]. Copyright 2018, American Association for the Advancement of Science. d) A hydrogel MAM robot designed with asymmetrical cavities that change shape under varying hydraulic pressure, resulting in material bending. Readapted with permission[116g]. Copyright 2018, IOP publishing.