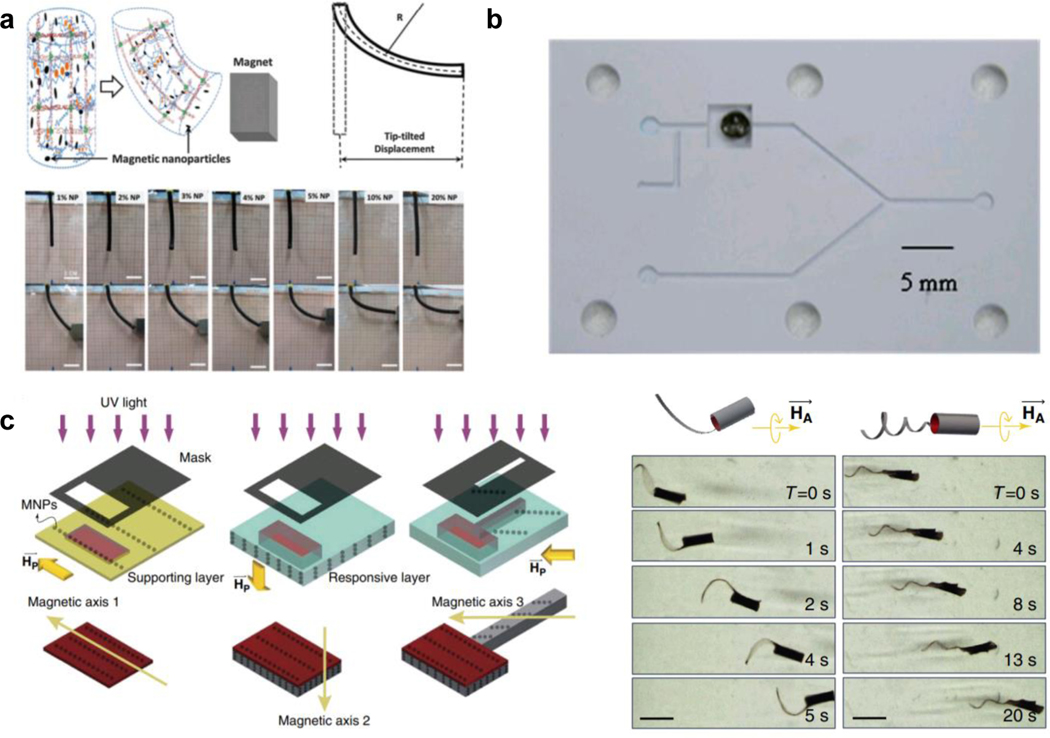
Figure 8. Magnetic field responsive MAMs.
a) Polyacrylamide hydrogel MAMs embedded with randomly distributed MNPs. This material shows a very strong response, bending in the direction of an applied magnetic field even at low MNP contents. Readapted with permission[95a]. Copyright 2015, Royal Society of Chemistry. b) Fe3O4/pNIPAM composite (black dot) that can open/close a microfluidic channel upon the application of alternating magnetic field. This field heats the iron oxide particles, causing the deswelling of the pNIPAM polymer that opens the channel. Readapted with permission[96a]. Copyright 2009 Royal Society of Chemistry. c) (left) Magnetic responsive MAMs can also be fabricated with pre-organized MNPs. This induces sensitivity to the orientation of an applied magnetic field (right), resulting in a highly sensitive and controllable soft robot. Readapted with permission[97], Copyright 2016, Springer Nature.