Figure 9. Long-term immunity after subcutaneous immunization with 107 pfu rVSV-F, rVSV-G, or rVSV-G-2A-F.
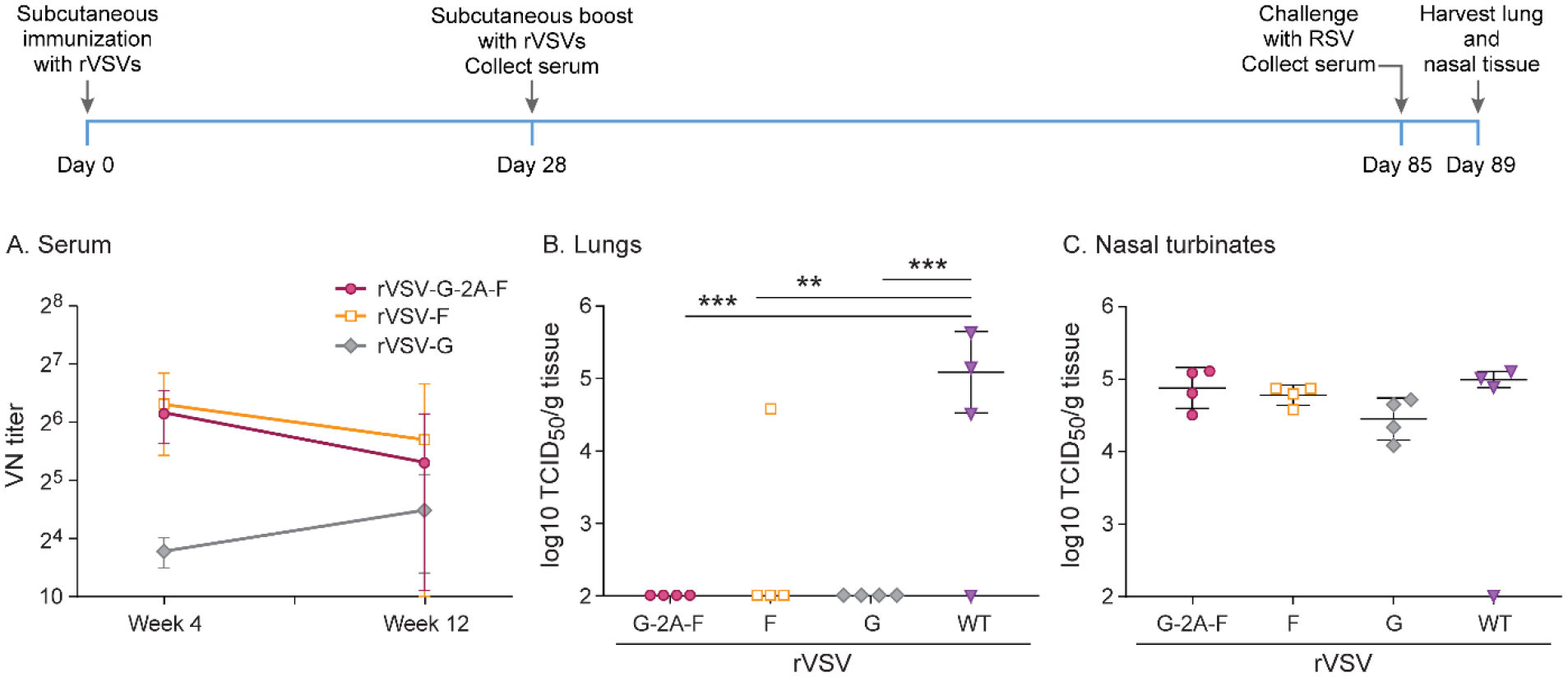
Cotton rats were immunized with 107 pfu rVSV-F, rVSV-G, or rVSV-G-2A-F via subcutaneous route, and then boosted with the same dose via the same route 4 weeks later. Cotton rats were challenged with RSV-A2 after a total of 12 weeks, and viral titers were assessed via TCID50, with the limit of detection at 2log10. Serum antibody levels were assessed via neutralizing antibody assay, with the limit of detection set at 10. A. Neutralizing titers against RSV in serum. Immunization with rVSV-G generated low levels of neutralizing antibodies that did not change over 12 weeks, while immunization with rVSV-F and rVSV-G-2A-F generated 4–5-fold higher levels of antibodies that slowly waned over the course of 12 weeks. B. RSV titer in lung homogenate. rVSV-F, rVSV-G, and rVSV-G-2A-F all provided complete protection against RSV A2 challenge. C. RSV titer in nasal homogenate. No treatment group was protected against RSV A2 challenge. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001
