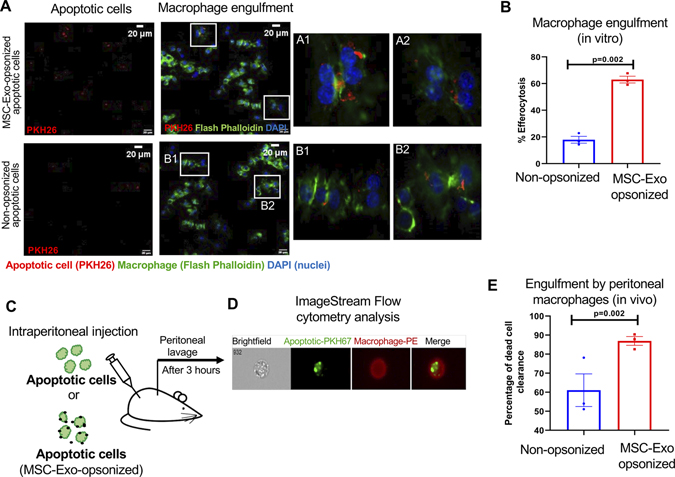
Figure 2. Binding of MSC-Exo to dead cells enhances its engulfment by macrophages.
A, Immunofluorescence staining showing uptake of apoptotic H9c2 cells (PKH26-labeled, red) by macrophage cell line, RAW 264.7 cells (Flash Phalloidin, green). DAPI to stain nuclei of RAW 264.7 cells (blue); Scale bar, 20 μm; Insets (A1 through B2) showing magnified images of macrophages ingesting apoptotic cells opsonized with and without exosomes. B, Graph showing that MSC-Exo opsonization enhances efferocytosis of dead cells, P=0.002. C, Schematic representation of in vivo efferocytosis assay. D, Representative image-stream analysis images for the in vivo efferocytosis assay (apoptotic cells labelled with PKH26, green; macrophages were labelled with PE conjugated F4/80 antibody). E, Graph showing that MSC-Exo opsonization enhances engulfment of dead cells by peritoneal macrophages represented as % dead cell clearance. n=3, P=0.002.