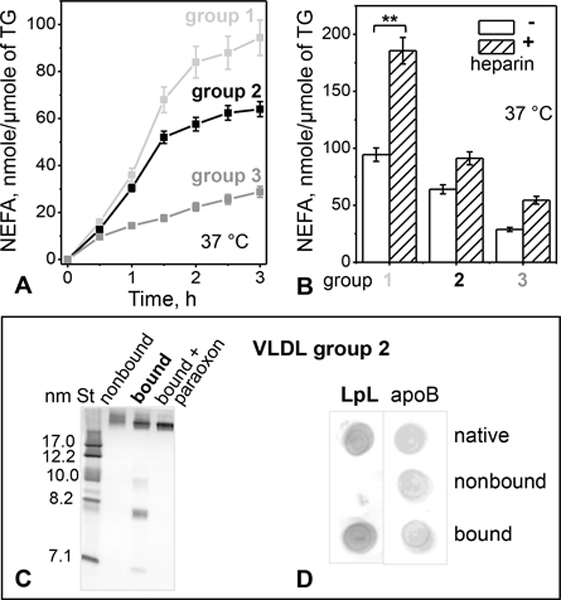
Figure 4.
LpL-dependent hydrolysis of TG in VLDL.
(A) Time course of lipolysis by the endogenous VLDL-bound LpL. VLDLs (0.3 μmole TG) from groups 1 – 3 were incubated without or with paraoxon (2 mmol/ml) at 37 °C for to 3 h. NEFA were measured at indicated time points; the blanks (with LpL inhibited by paraoxon) were subtracted from the data (without paraoxon). The results are shown as the mean ±SEM of three independent measurements.
(B) Heparin augments TG hydrolysis by the endogenous VLDL-bound LpL. VLDL (0.3 μmole TG) was incubated with heparin (0.3 μg/ml) at 37 °C for 3 h, the reaction was stopped with paraoxon (2 mmol/ml), whereupon NEFA were quantified. Values are shown as the mean ±SEM of three independent measurements; p≤0.1 (**), p≤0.05 (***).
(C) Non-denaturing PAGE of group 2 VLDL 6 hours after fractionation by heparin affinity chromatography. Non-bound fraction, bound fraction without or with paraoxon, and molecular size standards (St) are shown.
(D) Dot blot of VLDL 6 hours after fractionation by heparin affinity (same as in panel C) using antibodies for LpL and apoB.