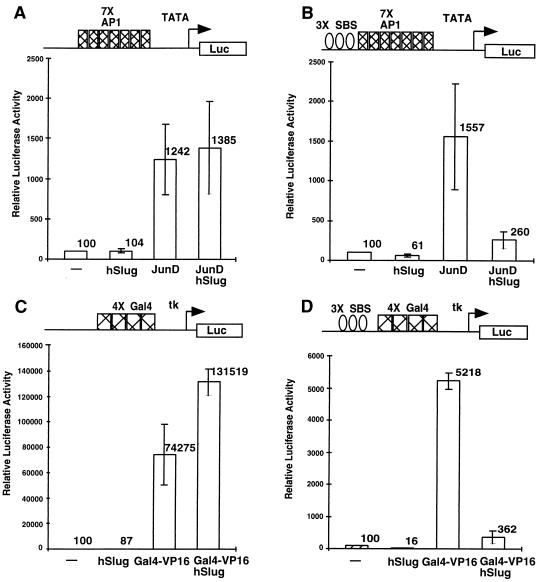
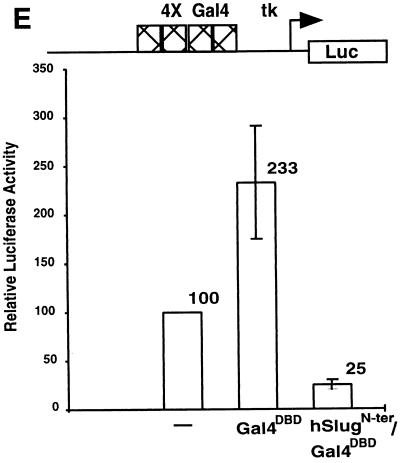
FIG. 4.
Repression of basal and activated transcription by hSlug. Human 293T cells were transfected with different combinations of expression and reporter plasmids. The specific DNA-binding sites on the promoter of the reporter plasmids used are illustrated at the top of each panel. Luciferase reporter activities were measured 48 h after transfection. In the presence of appropriate binding sites, JunD (A) and Gal4-VP16 (C) increased the reporter activity substantially, indicating activation of transcription. The addition of hSlug did not repress transcription if the binding sites for hSlug were not present (A and C). In the presence of the SBS, hSlug repressed the activated transcription by both JunD and Gal4-VP16 (B and D). Furthermore, the basal transcription was also repressed significantly by hSlug (B and D). Panel E shows that a fusion construct, the hSlug N terminus fused with the Gal4 DBD, repressed basal transcription. The reporter contained the Gal4 binding sites and was modestly activated by the GAL4 DBD alone. Therefore, occupation of the binding sites by the hSlug fusion reduces the activity to a level much lower than the basal level, suggesting active repression.