Figure 3: Potential analytical workflows.
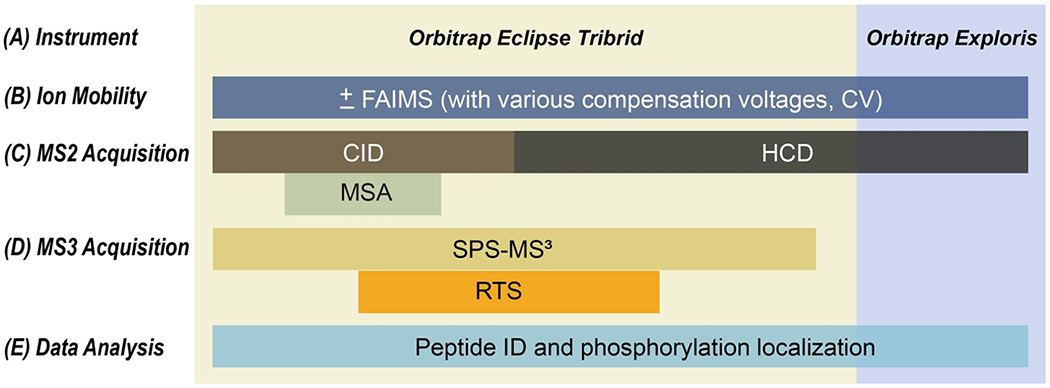
Various modalities are possible for the analysis of enriched phosphopeptides. A) The overall architecture of the instrument may limit the options for data acquisition. Such limitations are specifically with respect to mass analyzers, as high-resolution mass analyzers are required to detect mass differences of 6 mDa between isotopologue pairs of isobaric reagents. B) Ion mobility (such as FAIMS) can add an orthogonal dimension of separation. Alternating the number and value of compensation voltages (CVs) can enhance phosphoproteome coverage. C) Options for MS2 acquisition can include CID, CID-MSA, or HCD fragmentation on Tribrid mass spectrometers - such as the Orbitrap Fusion, Lumos, and Eclipse mass spectrometers), but commercial Orbitrap Exploris and Q-Exactive instruments are limited to only HCD fragmentation. D) Tribrid mass spectrometers also allow for MS3 scan-based quantification. In addition, newer instruments can leverage the advantages of real-time database searching (RTS). E) A variety of data analysis strategies are possible including various search engines and probability-based algorithms to determine phosphorylation site localization.
