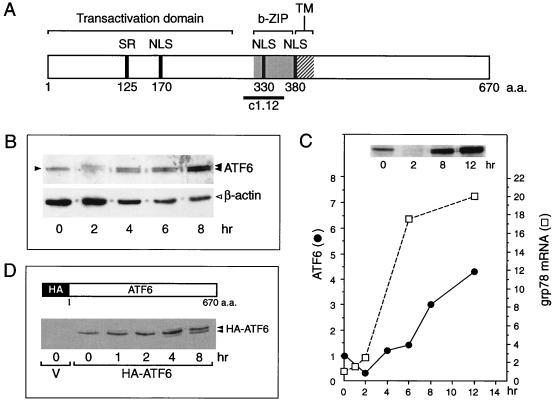
FIG. 1.
Tg stress-induced changes of ATF6. (A) Schematic drawing of the primary structure of ATF6, a 670-amino-acid (a.a.) protein. The positions of the transactivation domain, the b-ZIP domain, and a putative transmembrane (TM) domain are in brackets. The locations of the serine-rich (SR) region, putative nuclear localization signal (NLS), and the subfragment c1.12 used to generate antibody against the basic region of ATF6 are also indicated. (B) Total cell lysates were prepared from NIH 3T3 cells treated with Tg for the indicated time and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-ATF6 antibody. Twenty micrograms of each protein sample was applied to each lane. The single 90-kDa ATF6 band (at time zero) is indicated by a single closed arrowhead and the ATF6 doublet band in the later time points is marked by the double arrowheads. The β-actin protein band (open arrowhead) in the same Western blot served as the protein loading control. (C) The level of ATF6 following Tg stress was quantitated by densitometry and plotted against the kinetics of accumulation of the grp78 mRNA. The measurement of grp78 mRNA levels in Tg-treated NIH 3T3 cells has been described elsewhere (13). A Western blot of ATF6 protein level after 0, 2, 8, and 12 h of Tg treatment is shown in the inset. Fifty micrograms of each protein sample was applied to each lane. (D) Schematic drawing of HA-tagged full-length ATF6 (36). Shown below is the Western blot with anti-HA antibody performed on total cell lysate prepared from Cos cells transfected with empty vector (V) or with HA-ATF6 expression vector and treated with Tg for the indicated time. The position of the HA-ATF6 doublet is indicated.