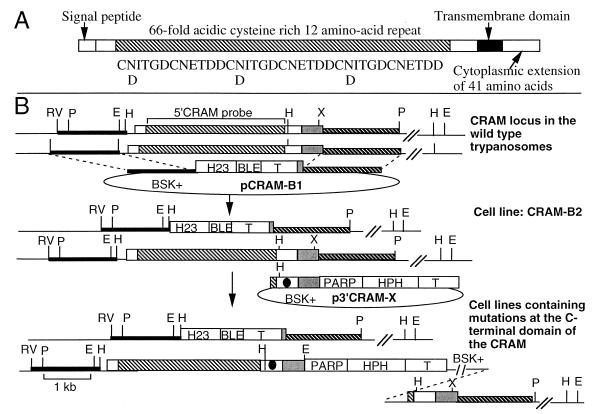
FIG. 1.
Physical maps of the CRAM locus in wild-type trypanosomes and CRAM mutant cell lines. (A) Schematic diagram of the structure of CRAM. The amino acid sequence of three contiguous cysteine-rich 12-amino-acid repeats is listed underneath the repeat domain (the shaded box region). (B) Top, structure of the CRAM locus in wild-type trypanosomes and plasmid pCRAM-B1. The large boxed region represents the CRAM gene. The open white boxes at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the CRAM gene represent the unique N- and C-terminal peptide regions, respectively; the shaded box represents the reptitive peptide region; the gray box represents the 3′ UTR of the CRAM gene. pCRAM-B1, containing the ble gene flanked by the hsp70 intergenic region promoter (H23 [27]) and the βα-tubulin intergenic region (51), was used for gene replacement. In pCRAM-B1, the 5′ targeting sequence containing the HindIII/EcoRV fragment derived from the 5′ flanking region of the CRAM locus (black bar) and the 3′ targeting sequence encodes the XhoI/PstI fragment of the 3′ flanking region of the CRAM locus (hatched bar). Middle, structure of the CRAM locus in CRAM-B2 cell line and p3′CRAM-X plasmids. One allele of the CRAM gene in the CRAM-B2 cell line was deleted and replaced by the H23-ble gene. The p3′CRAM-X plasmids, containing the hph gene flanked by the PARP promoter and the βα-tubulin intergenic region, were used for gene integration. The sequence spanning the 3′ end of the CRAM gene was used as a targeting sequence. The black dot indicates the mutation carried in the 3′ coding region of each of mutated CRAM genes. The HindIII site was used to linearize the plasmid for integration of the plasmid into the 3′ coding region of the CRAM gene. Bottom, structure of the CRAM locus of cell lines containing a mutated CRAM gene. Abbreviations: PARP, the PARP gene promoter and its 3′ splice site (41); T, intergenic region of βα-tubulin genes (51); BSK+, the plasmid vector Bluescript SK+; HPH, the hph gene; BLE, the ble gene (purchased from CAYLA Inc.); double slashes, undetermined distance; H, HindIII; E, EcoRI; P, PstI; RV, EcoRV; X, XhoI. The 5′ CRAM probe used in hybridizations is indicated at the top.