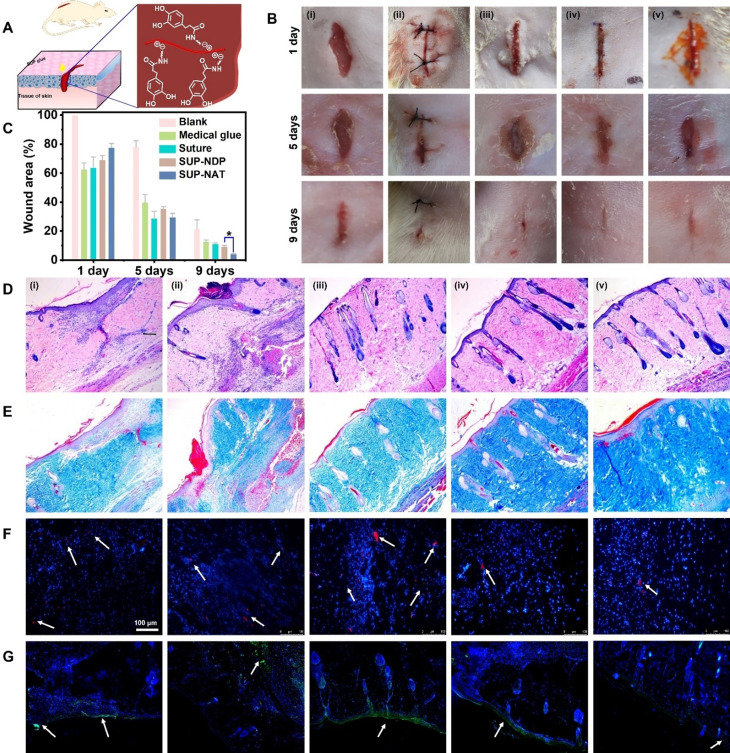
Figure 4.
Wound sealing and healing investigated in a rat model treated with SUP glues. A) Schematic representation of SUP glue application in vivo for healing of linear wounds. K‐NDP and K‐NAT glues were used for the experiments. B) Photographs of the wounds after 1, 5, and 9 d on rat skin. Different treatments were used for in vivo wound healing experiments. (i) blank (no treatment), (ii) suture closure, (iii) commercial medical adhesive COMPONT®, (iv) K72‐NDP glue, and (v) K72‐NAT glue. SUP glue facilitates wound healing and tissue regeneration in a 9‐day wound‐healing experiment. The scale bar is 10 mm. C) Quantitative analysis of SUP glue treatment over time monitoring the wound closure area. Three trials were performed for each measurement. Statistics were evaluated by t‐test. (* p=0.022 <0.05). D) H&E staining to investigate tissue regeneration. E) Masson's trichrome staining indicating collagen deposited within the defects. F–G) Immunofluorescence analysis of IL‐6 and TNF‐α. Red immunofluorescent staining and green immunofluorescent staining as an indicator of the levels of IL‐6 and TNF‐α (marked by white arrows), respectively. The scale bar is 100 μm.