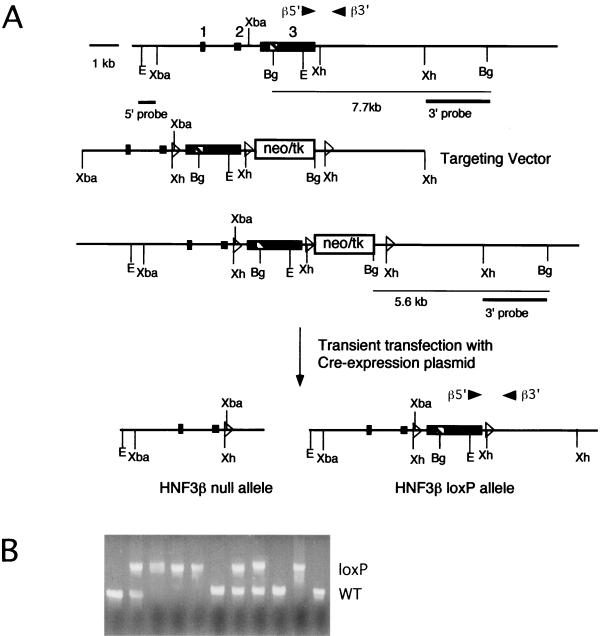
FIG. 1.
Cre-loxP-mediated targeting of the HNF3β gene and generation of homozygous HNF3βloxP/loxP mice. (A) Targeting vector for the HNF3βloxP allele. Primers β5′ and β3′ were used in PCR genotype analysis. (First line) Gene structure of the endogenous HNF3β locus. Exons are indicated as boxes, the striped box represents the winged helix domain, open triangles represent loxP sites, and arrow heads represent primer positions. (Second line) Targeting vector which introduces a cassette containing the neomycin-herpes simplex virus-thymidine kinase selection cassette (neo-tk) flanked by loxP sites downstream of exon 3. An additional loxP site was introduced in the intron upstream of exon 3. (Third line) Gene structure of homologous recombinants. The 3′ probe was used for the Southern blot analysis (data not shown). (Fourth line) Cre-mediated deletion results in either the HNF3β null allele (deletion of exon 3) or the HNF3βloxP allele (exon 3 flanked by loxP sites). Abbreviations: Bg, BglII; E, EcoRI; Xh, XhoI; Xba, XbaI. (B) HNF3βloxP/loxP mice are viable and healthy. Shown are the results of PCR genotype analysis of a litter from mating HNF3βloxP/+ heterozygotes inter se. The HNF3βloxP allele segregates in expected Mendelian frequency. WT, wild type.