FIGURE 1.
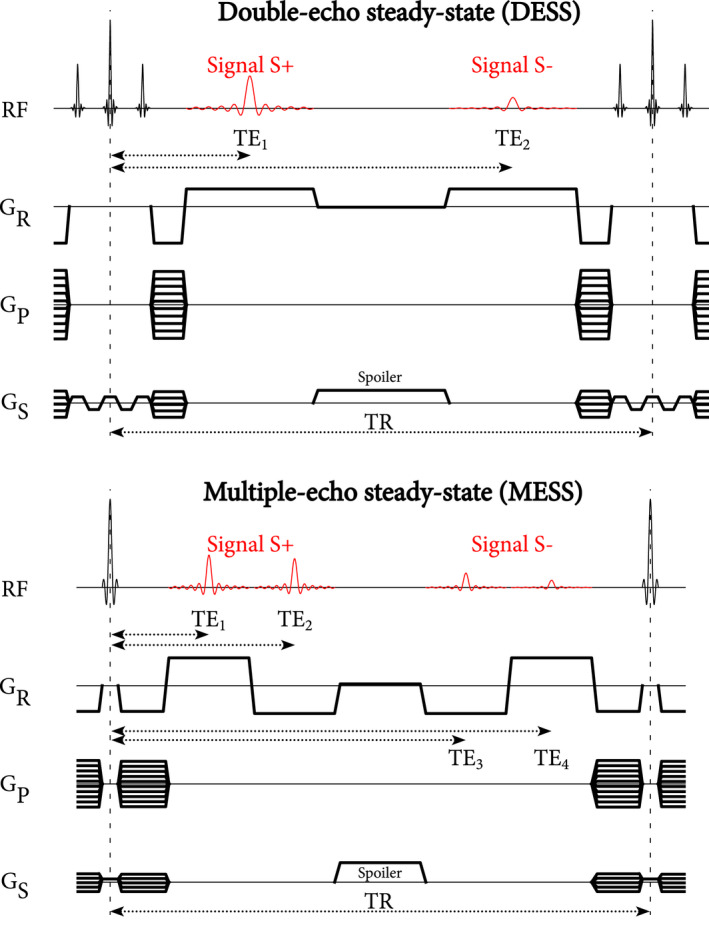
Pulse sequence diagrams for DESS (top) and MESS (bottom). The S+ signal is comparable to an FID signal, whereas the S− is more T2‐weighted and originates from spin echo and stimulated echo pathways. In the same TR, MESS acquires two additional echoes with bipolar readouts. DESS uses a chemically selective binomial RF pulse, whereas MESS uses a standard RF pulse. In both sequences a spoiler gradient is included in the slice direction. During the spoiler, a small gradient is active in the readout direction to compensate for the area of the ramp‐down and ramp‐up of the readouts. Note that, because we implemented DESS and MESS as modified three‐echo and five‐echo GRE sequences with fixed echo spacing, the spoiler duration was 1.56 ms longer in DESS
