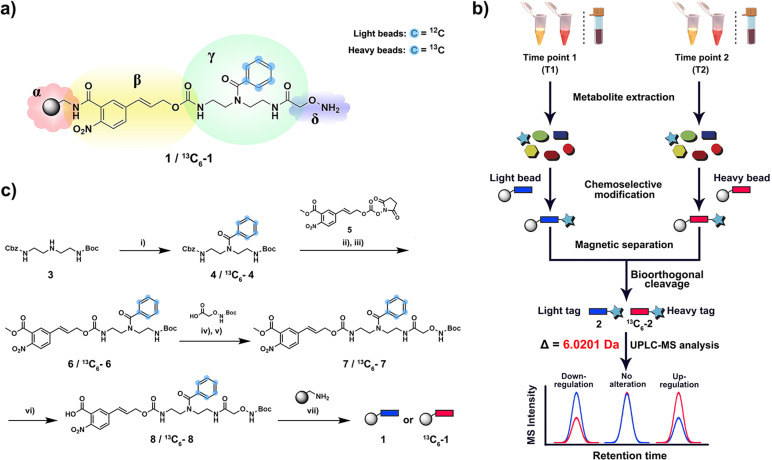
Figure 1.
Chemoselective probe for quantitative analysis of metabolites in human samples. a) Chemical structure of chemoselective probe (1 and 13C6−1) immobilized to magnetic beads. α=amino‐activated magnetic beads, β=bioorthogonal cleavage site, γ=metabolite tag containing isotope‐labeled moiety, δ=reactive site. b) Schematic workflow for analysis of human urine, plasma and fecal samples. After metabolite extraction, the metabolome of two different samples is treated with either “light” (1) or “heavy” beads (13C6–1). After separation of captured metabolites, bioorthogonal cleavage of both combined bead types releases tagged metabolites for UPLC‐MS analysis. c) Chemical synthesis of chemoselective probe and immobilization to magnetic beads. Reagents and conditions: i) benzoyl chloride 1.2 equiv, Et3N 3.0 equiv, DCM, room temperature (r.t.) 3 h. ii) Pd/H2, MeOH, r.t., 5 h. iii) N,N‐Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) 3.0 equiv, DCM, r.t., 5 h. iv) Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA)/ DCM 1:1, r.t., 2 h. v) 2‐(1H‐Benzotriazol‐1‐yl)‐1,1,3,3‐tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HBTU) 1.2 equiv, hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT) 1.1 equiv, DIPEA 3.0 equiv, DCM, r.t., 16 h. vi) 2 M aqueous LiOH, MeOH/H2O 1:1, r.t., 30 min. vii) PyBop 1.5 equiv, HOBT 1.1 equiv, DIPEA 3.0 equiv, DMF/DCM 1:1, r.t., 16 h.