Figure 1. Clonal complex-specific LukAB variants exhibit different cytotoxic activities towards human leukocytes.
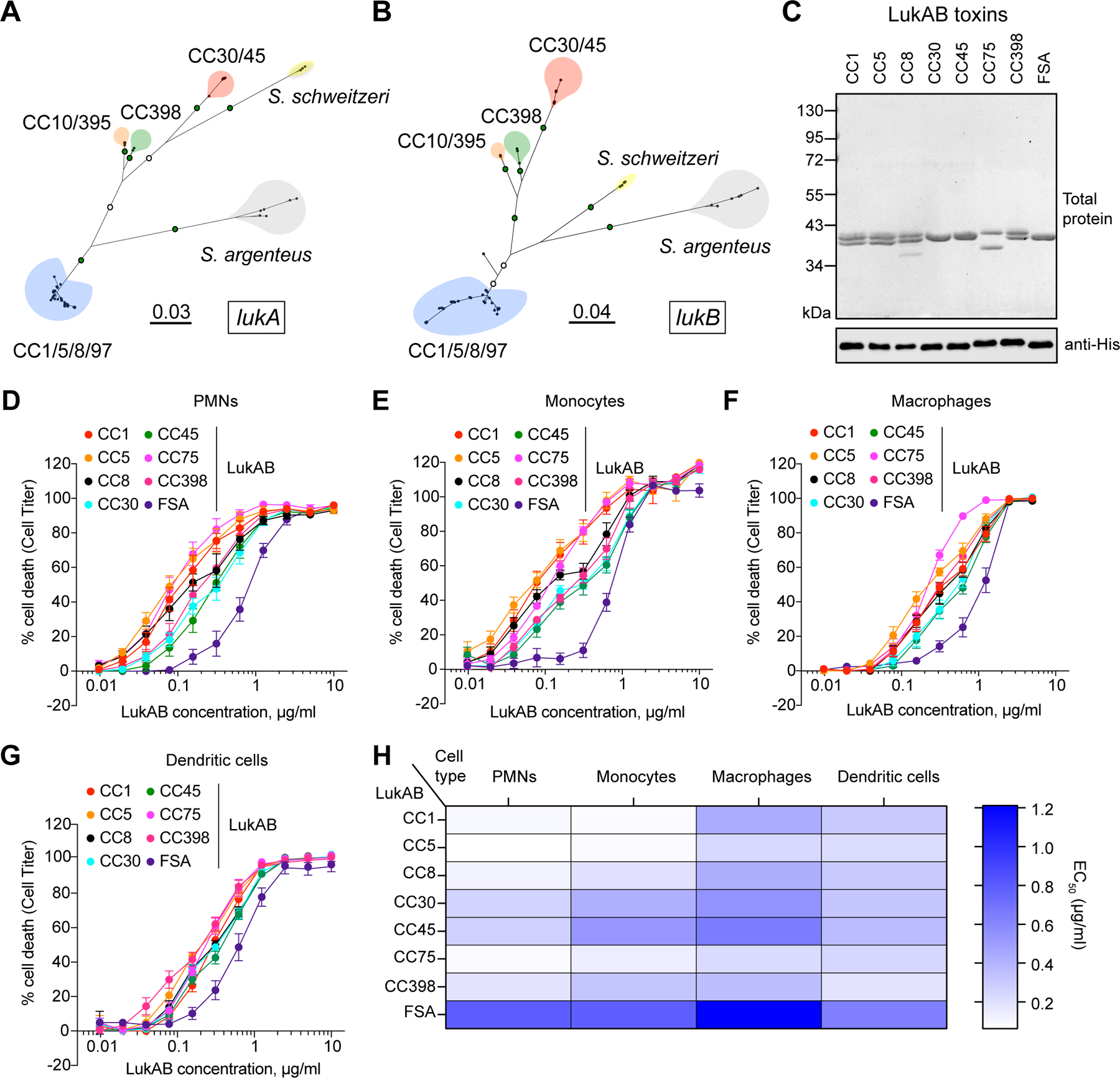
A-B: Unrooted maximum likelihood phylogeny for lukA (A) and lukB (B). Branch lengths are in substitutions/site. Key bootstrap values are depicted in green (>90%) or white (>70%) on branches. Major clades are colored blue (CC1/5/8/97), red (CC30/45), orange (CC10/395), green (CC398), yellow (S. schweitzeri, FSA), and grey (S. argenteus, CC75). C: Recombinant co-purified 6xHis-LukA and LukB proteins visualized by total protein staining (1 μg) and immunoblotting (100 ng) with anti-His antibody. One replicate of this experiment was performed. D-G: Intoxication of primary human PMNs (D), monocytes (E), macrophages (F), and dendritic cells (G) with indicated concentrations of LukAB toxins and cell viability measured with Cell Titer. Data were collected using cells isolated from six independent donors (PMNs), four donors (monocytes), five donors (monocyte-derived macrophages), four donors (monocyte-derived dendritic cells), and are represented as mean values ±SEM. H: Half-maximal lytic concentrations (EC50) of each toxin calculated from data presented in panels D-G. Also refer to Extended Data Figures 1–2 and Supplementary Tables 1–2.
