Figure 4. CC30 S. aureus kills leukocytes in a LukAB and HVCN1 dependent manner.
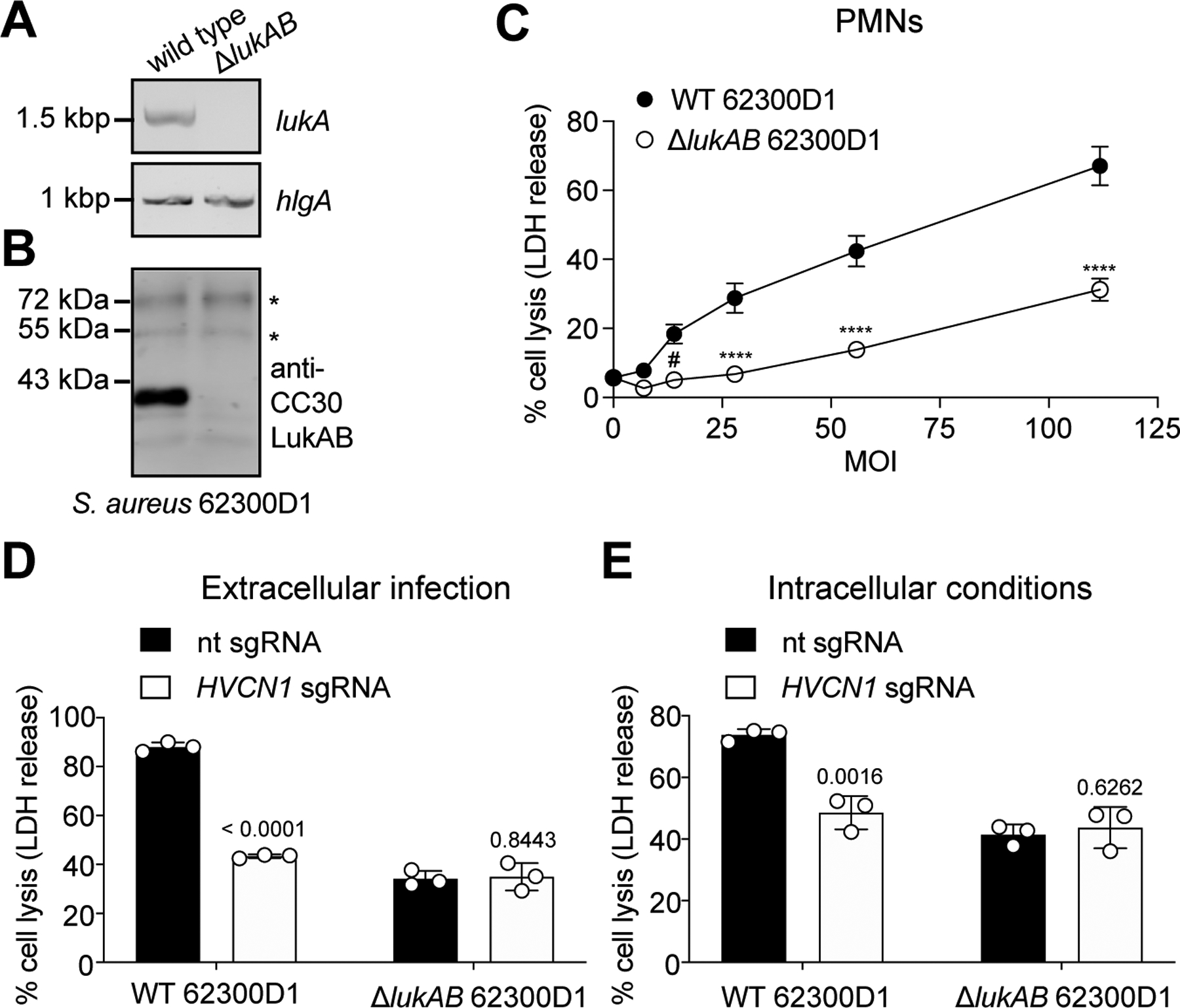
A-B: PCR targeting lukA and hlgA (A) and immunoblot of CC30 LukAB in supernatants of wild type and ΔlukAB CC30 S. aureus 62300D1 (B). Asterisks indicate non-specific bands that serve as loading controls. One replicate of this experiment was performed (A). Representative image of two independent experiments is shown (B). C: Viability of human PMNs following a 2-h infection with nonopsonized wild type (WT) or isogenic ΔlukAB CC30 S. aureus 62300D1 at the indicated multiplicity of infection (MOI). PMN lysis measured by LDH release. Data are from PMNs isolated from six independent donors represented as the mean values ±SEM. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA (****, P ≤ 0.0001; #, P = 0.0119). D-E: Viability of ITGAM shRNA THP1 cells transduced with lentiCRISPRv2 expressing non-targeting (nt) sgRNA or HVCN1 sgRNA and infected with nonopsonized (extracellular infection, D) or with opsonized (intracellular conditions, E) WT and ΔlukAB CC30 S. aureus 62300D1 for 2h (MOI=100). THP1 cell lysis was measured by LDH release. Data from three independent experiments are represented as the mean ±SD. Statistical significance was determined by t-test (two-tailed), numbers indicate P values.
