FIGURE 5.
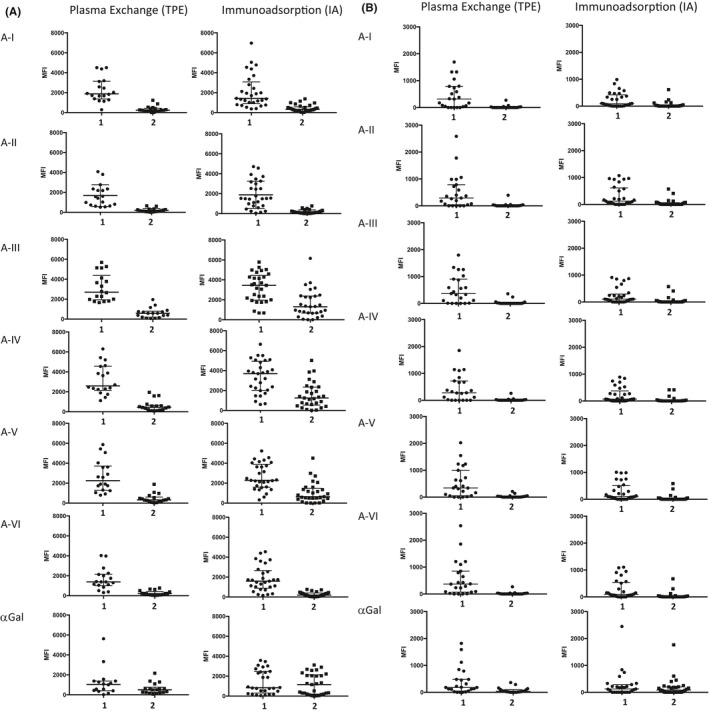
A‐subtype‐specific antibodies in ABO‐O patients undergoing plasma exchange or immunoadsorption measured at timepoints 1 and 2. (A) IgG antibodies. At timepoint 1, IgG binding to any A‐subtype was not significantly different between the cohorts that subsequently underwent EART by plasma exchange and by antigen‐specific immunoadsorption. At timepoint 2 there was a significant reduction in IgG binding to all A‐subtypes (p < .001). IgG binding to αGal was reduced only by plasma exchange. There was no significant difference between plasma exchange and antigen‐specific immunoadsorption with respect to IgG binding to A‐I, II and VI at timepoint 2 (p > .3), whereas IgG binding to A‐III, IV, and V was significantly higher in the group treated with immunoadsorption (p ≤ .006). Data points on individual patients, and lines showing median and interquartile range in this and all subsequent dotplots. (B) IgM antibodies. At timepoint 1, IgM binding to A‐subtypes was not significantly different in the plasma exchange group except for A‐III which reached statistical significance (p = .04). There was no significant difference between plasma exchange and antigen‐specific immunoadsorption with respect to IgM binding to any A‐subtypes at timepoint 2 (p ≥ .4)
