FIGURE 4.
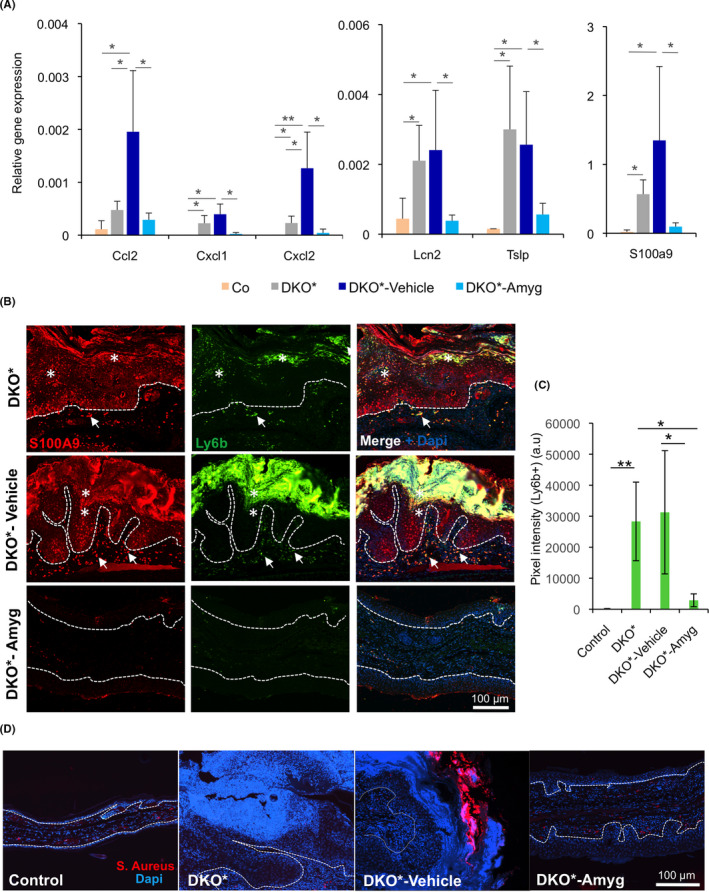
FIB‐116 cream reduces neutrophil recruitment in skin and reduces antimicrobial peptides towards baseline expression in DKO* treated mice. (A) Gene expression of neutrophil recruitment chemokines Ccl2, Cxcl1 and Cxcl2 and antimicrobial peptides Lcn2, S100a9 and Tslp of the ear samples from control (WT), DKO* without treatment, DKO*‐Amygdalin, DKO*‐Vehicle mice after 14 days of treatment. n > 5 per group. Statistical significance *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA, one‐tailed test). (B and C) Representative immunofluorescence images of ear section from DKO* without treatment, DKO*‐Amygdalin, DKO*‐Vehicle mice after 14 days of treatment. Green (Ly6b), Red (S100A9) and blue (Dapi). Epidermal overexpression of S100A9 in DKO* and DKO*‐vehicle mice, whereas animals treated with amygdalin cream reduce its expression. Neutrophil infiltration (Ly6b+ S100A9+) increases in the dermis (arrows) and epidermis (asterisks) of animals DKO* and DKO*‐vehicle mice, whereas the number of neutrophils in mice treated with amygdalin cream reduces dramatically (C, a.u. = arbitrary unit). n = 3 per group. Dotted lines separate epidermis and dermis. (D) Representative immunofluorescence images for Staphylococcus aureus of ear section from control (WT), DKO* without treatment, DKO*‐Amygdalin, DKO*‐Vehicle mice after 14 days of treatment. Red (S. Aureus) and blue (Dapi). n = 3 per group. Dotted lines separate epidermis and dermis
