FIG 5.
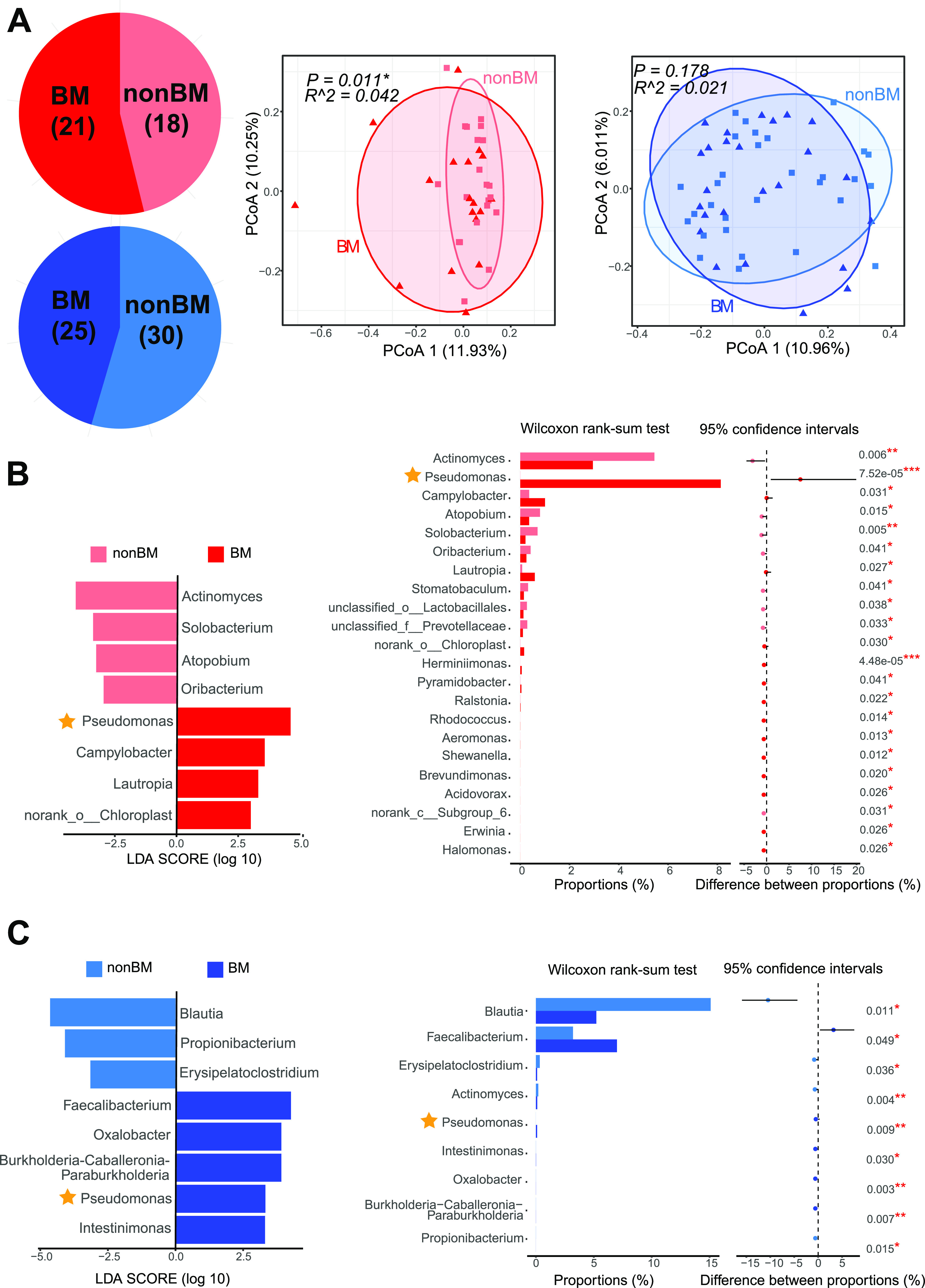
Patients with brain metastasis differed significantly from other distant metastasis in microbial profiles of the sputum and feces. (A) Numbers of sputum (red) and gut (blue) brain metastasis samples (left); BM, NSCLC patients in stage IV with brain metastasis; non-BM, stage IV NSCLC patients without brain metastasis. A principal-coordinate analysis showed differences in beta-diversity between BM and non-BM in sputum (middle) but not in the gut (right). LEfSe (left) analysis and Wilcoxon rank sum test (right) of differentially abundant microbial biomarkers between BM and non-BM in sputum (B) and the gut (C). Level of significance: ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05; NS, P ≥ 0.05. The star indicates that the genus Pseudomonas was significantly different in abundance.
