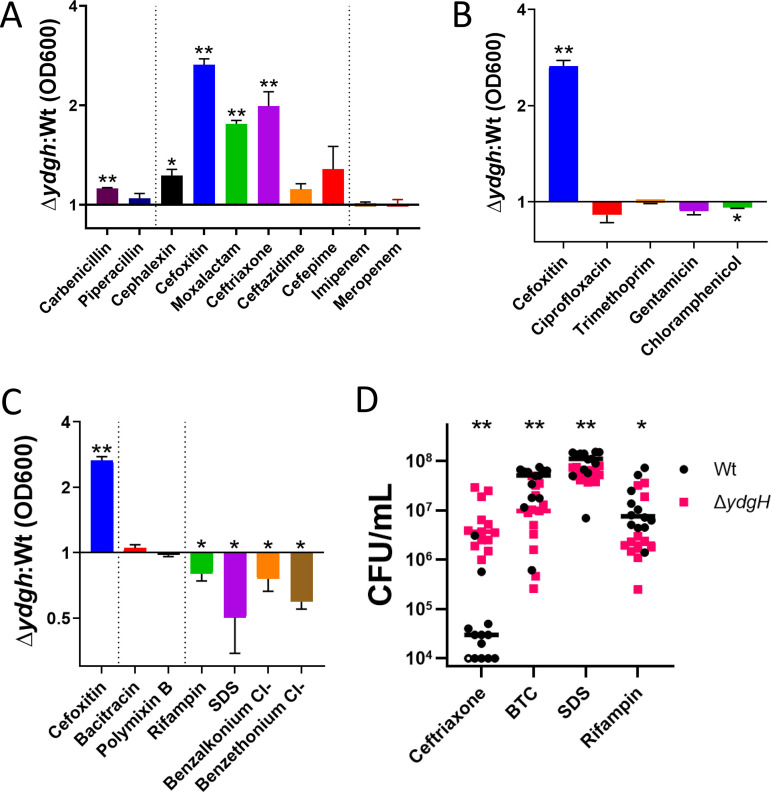
FIG 5.
YdgH deletion leads to decreased cephalosporin susceptibility and increased detergent susceptibility. (A) OD600 ratios demonstrating that the ΔydgH mutant has decreased second- and third-generation cephalosporin susceptibility (including to cefoxitin, moxalactam, and ceftriaxone) but no large differences in susceptibility to first-generation cephalosporins, antipseudomonal cephalosporins, penicillins, or carbapenems. (B) OD600 ratios demonstrating that the ΔydgH mutant has no large differences in non-beta-lactam antibiotic susceptibility. Cefoxitin ratio reproduced for reference. (C) OD600 ratios demonstrating that the ΔydgH mutant has no large differences in bacitracin or polymyxin susceptibility, but has small but significant increases in susceptibility to rifampin, and more broadly to the detergents sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), benzethonium chloride, and benzalkonium chloride. Cefoxitin ratio reproduced for reference. (D) Viability experiments of the Wt and the ΔydgH mutant in ceftriaxone, benzethonium chloride (BTC), sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and rifampin confirmed the results of the turbidity experiments. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; unpaired two-tailed t test (A, B, and C) or Wilcoxon rank-sum test (D), unadjusted.