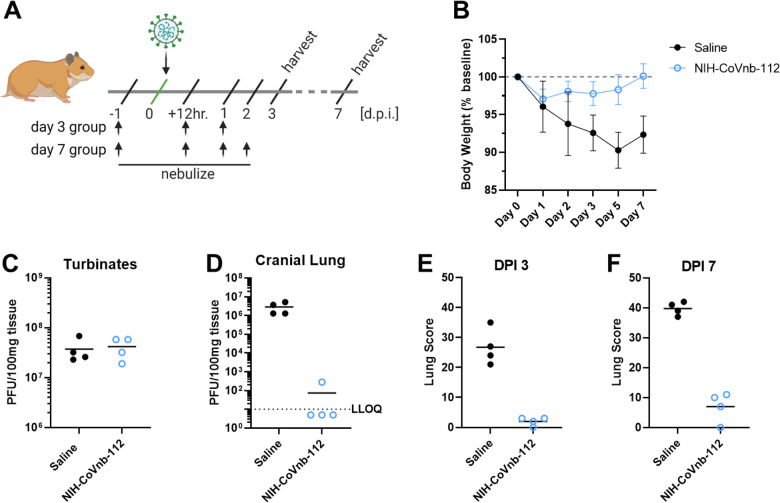
Figure 5. NIH-CoVnb-112 nebulization treatment in a hamster model of SARS-CoV-2.
(a) Schematic overview of study design for nebulization treatment of Syrian hamsters with NIH-CoVnb-112. Adult Syrian hamsters (n=8/group, males, 12 weeks old) were treated at −24 hours prior to virus challenge with nebulized saline or NIH-CoVnb-112 (25mg/mL) in a 5mL volume over 20 minutes. Following intranasal challenge, each group was treated at 12 hours post infection with the same condition, and again at 1 dpi. Half of the animals in each group received a fourth dose at 2 dpi. Animals were weighed daily and oral swabs taken at dpi 1–3. Groups were euthanized at day 3 and day 7 post infection respectively and sample taken for assessment. (Figure elements generated using BioRender.com) (b) Body weight change as a percentage of baseline weight for day 7 post infection group (n=4/group, mean +/− SD) (c) Viral burden from turbinate tissue of the day 7 post infection group as determined by double plaque overlay assay. (d) Viral burden from cranial lung tissue of the day 7 post infection group as determined by double plaque overlay assay. (e-f) Hematoxylin and eosin-stained tissue sections from the day 3 and day 7 post infection animals were semi-quantitively scored by a pathologist blinded to condition using an established scoring metric. Metrics included overall lesion extent, bronchitis, alveolitis, pneumocyte hyperplasia, vasculitis, and interstitial inflammation; each on a 0–4 or 0–5 scale and scores summed. Detailed data for day 3 and day 7 post infection are shown in Supplementary Fig. 9.