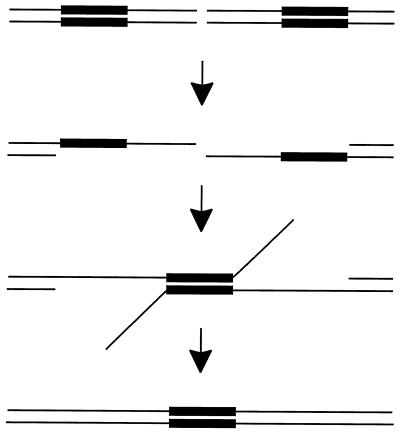
FIG. 1.
Single-strand annealing model. When a double-strand break is created in vivo, one strand on each side of the DSB is resected in the 5′-to-3′ direction, leaving a 3′ tail. When complementary sequences on opposite sides are exposed, they can anneal, forming a branched intermediate. The single-stranded tails are removed by a nuclease, the gaps are filled in, and any remaining nicks are ligated, finally resulting in a deletion product.