Figure 1. Depletion of DDX3X upregulates genes in the antiviral innate immune response.
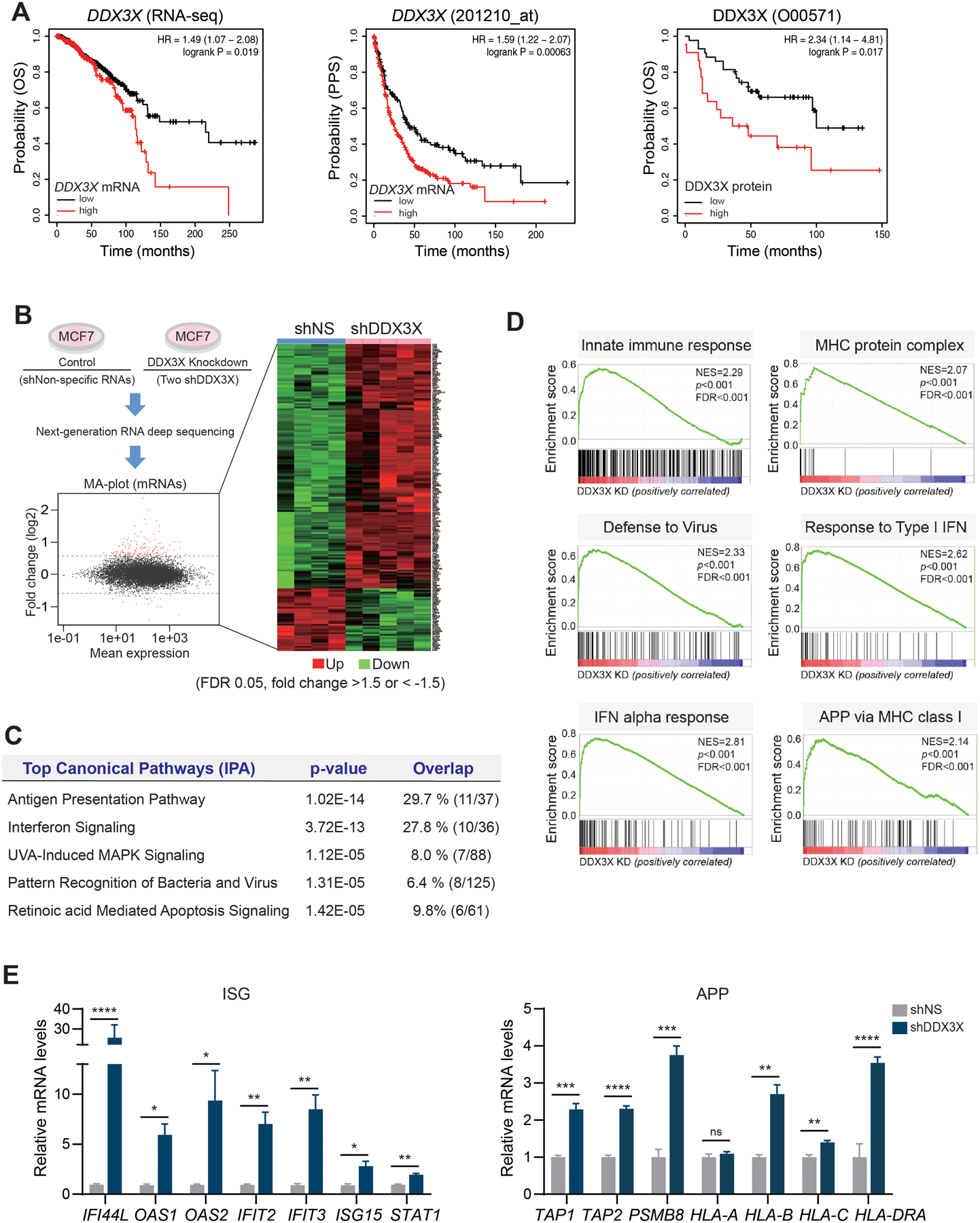
A. KM-plotter analysis shows that mRNA and protein levels of DDX3X are associated with a poor survival outcome in breast cancer. Overall survival (pan-cancer RNA seq), OS; Post- Progression Survival, PPS.
B. Genome-wide transcriptome analysis in DDX3X-control (shNS) or -knockdown (shDDX3X) MCF7 cells using a next-generation RNA deep sequencing. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (FDR 0.05, fold change >1.5 or < −1.5) in shNS vs. shDDX3X are shown in an MA-plot (labeled in red) and in a heat map.
C. Top canonical pathways of DEGs between DDX3X-control and -knockdown (KD) MCF7 cells.
D. GSEA analysis of DEGs between DDX3X-control and -KD MCF7 cells.
E. qRT-PCR of ISGs and APP gene expression in DDX3X-control or -KD MCF7 cells.
A non-specific shRNA (shNS); DDX3X targeting shRNAs (shDDX3X). Data are representative of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was calculated using unpaired t-tests. *p < 0.05; **p<0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant.
