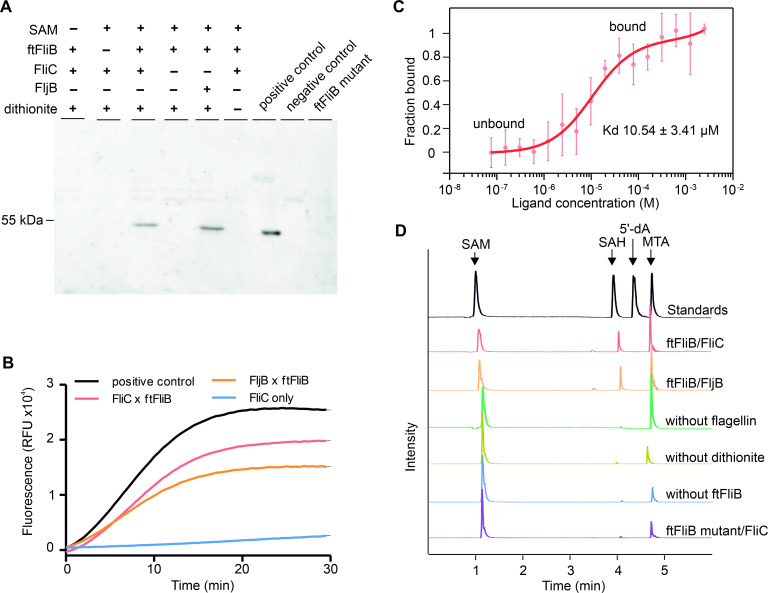
Fig 3. In vitro FliB methylation activity.
(A) Activity assay using an anti-methylated Lysine antibody. Methylated flagella sheared from wild type S. enterica were used as positive control; unmethylated flagella sheared from S. enterica FliB knockout mutant were used as negative control. Reaction with ftFliB C17A C22A C26A C27A (ftFliB mutant) was conducted in a mixture of SAM, FliC and dithionite. (B) Continuous fluorescent methyltransferase assay, SAH was used as a positive control and buffer alone was used as background control. Methylase ftFliB was mixed with either FliC or FljB under reducing environment, and the generation of SAH was measured using enzyme coupled fluorescence assay with an excitation/ emission wavelength of 535/590 nm. (C) Ligand binding affinity test of ftFliB and SAM. Binding of methylation ligand SAM to 1 μM ftFliB was analyzed with label-free MST. Data were shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD) calculated from three independent experiments. (D) HPLC-MS analysis of the methylation assay products. The methylation reactions were performed by mixing the methylase (ftFliB) and flagellin under reducing condition: reaction between ftFliB and FliC as ‘ftFliB/FliC’; reaction between ftFliB and FljB as ‘ftFliB/FljB’, control reaction lack of flagellin as ‘without flagellin’, control reaction under non-reducing condition as ‘without dithionite’, control reaction without the methylase as ‘without ftFliB’, reaction of ftFliB mutant with flagellin as ‘ftFliB mutant/FliC’. Extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) of SAM (m/z 399 [M + H]+), SAH (m/z 385 [M + H]+), 5’-dA (m/z 252 [M + H]+), MTA (m/z 298 [M + H]+) from each reaction were merged in one trace. The chromatograms intensities are normalized to the most abundant EIC.