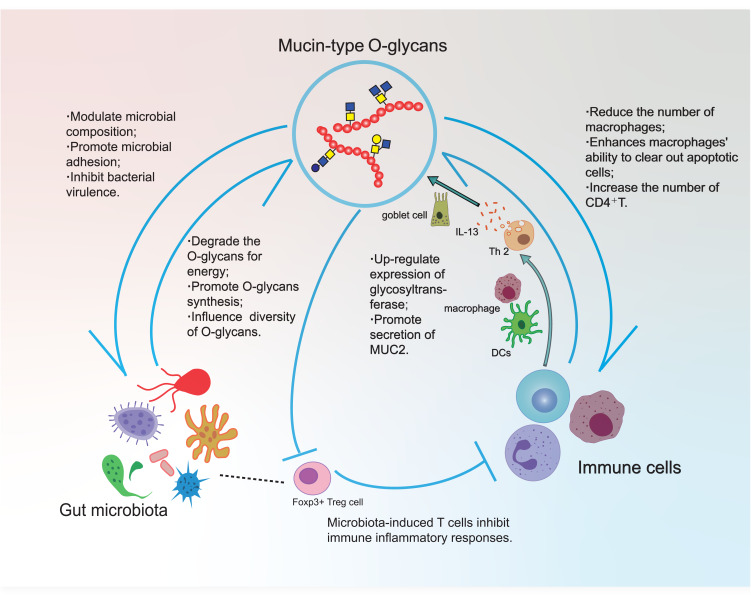
Figure 3.
Association between mucin-Type O-glycans, microbiota, and immune cells. O-glycans regulate microbial composition, promote microbial adhesion, and inhibit bacterial virulence. Conversely, intestinal flora can degrade glycan for energy and also affect the composition of glycan. O-Glycans not only affect the number of various immune cells in the body, such as macrophages and CD4+T cells but also enhance the ability of macrophages to remove apoptotic cells. Immune cells mainly secrete inflammatory factors to promote mucin glycosylation. Lack of glycosylation can also affect microbial-related regulatory T cells, thereby inhibiting immune responses.