Figure 4.
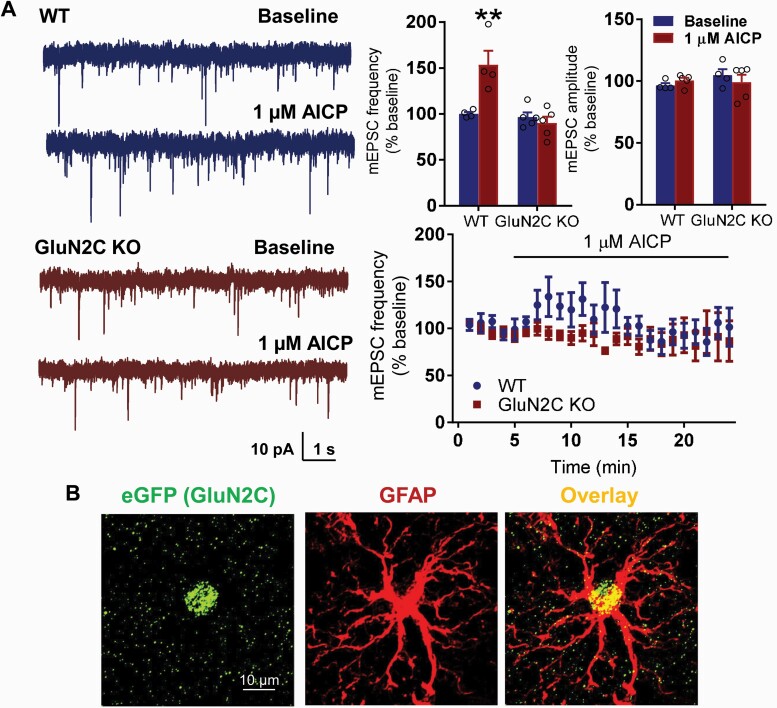
AICP increase excitatory neurotransmission in basolateral amygdala (BLA) neurons. (A) Whole cell voltage clamp recordings from BLA neurons were conducted in WT and GluN2C KO mice. A significant increase in the frequency of mEPSC was observed following bath application of AICP in WT mice (WT-baseline 100.117 ± 2.021 vs WT-1µM AICP 153.415 ± 15.345, P = .0016; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test). No significant differences were observed in amplitude of mEPSCs following AICP treatment (P > .05). AICP failed to produce any significant effect on mEPSC frequency and amplitude in GluN2C KO mice (P > .05). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. (B) Immunohistochemical analysis in Grin2CEGFP-CreERT2 (GluN2C KO) mouse model. The coronal sections passing through BLA were immunolabelled for eGFP (GluN2C) and GFAP. Expression of eGFP in the Grin2C-reporter model was found to primarily co-localize with astrocytic marker GFAP.