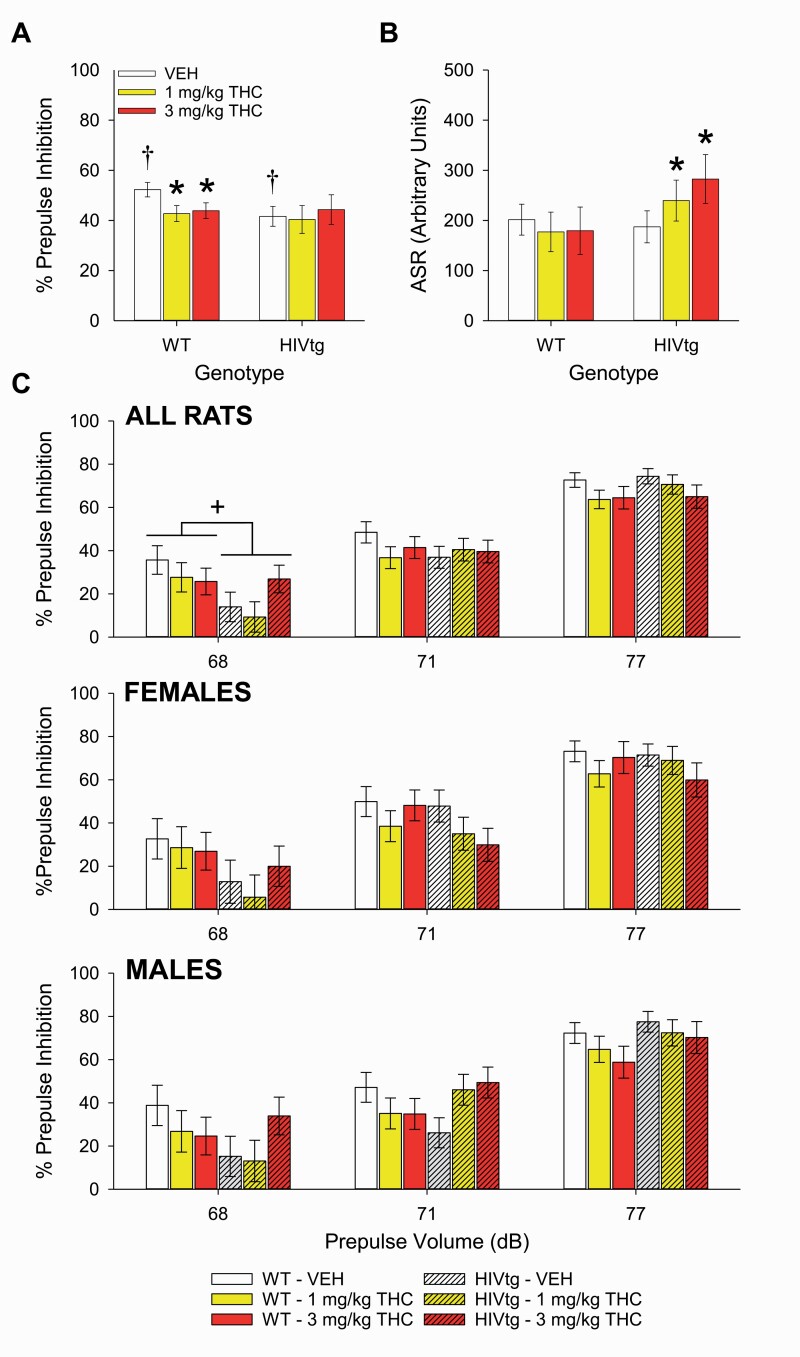
Figure 3.
The effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) on prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response (ASR) in male and female HIV transgenic (HIVtg) and wild-type (WT) rats. HIVtg rats displayed lower levels of PPI (averaged across prepulse intensities) following vehicle administration than WT rats. THC lowered PPI in WT rats only and did not affect HIVtg rats on this measure (A). THC affected ASR in HIVtg rats only, with both 1 and 3 mg/kg THC increasing ASR relative to vehicle (B). Follow-up analysis of a significant prepulse × genotype interaction revealed that HIVtg rats exhibited lower levels of PPI following 68-dB prepulses only (C) (top) regardless of sex (middle, bottom). +P < .05; *P < .05 vs vehicle; bars annotated with † significantly differ from each other (P < .05). Data presented as mean ± SEM.