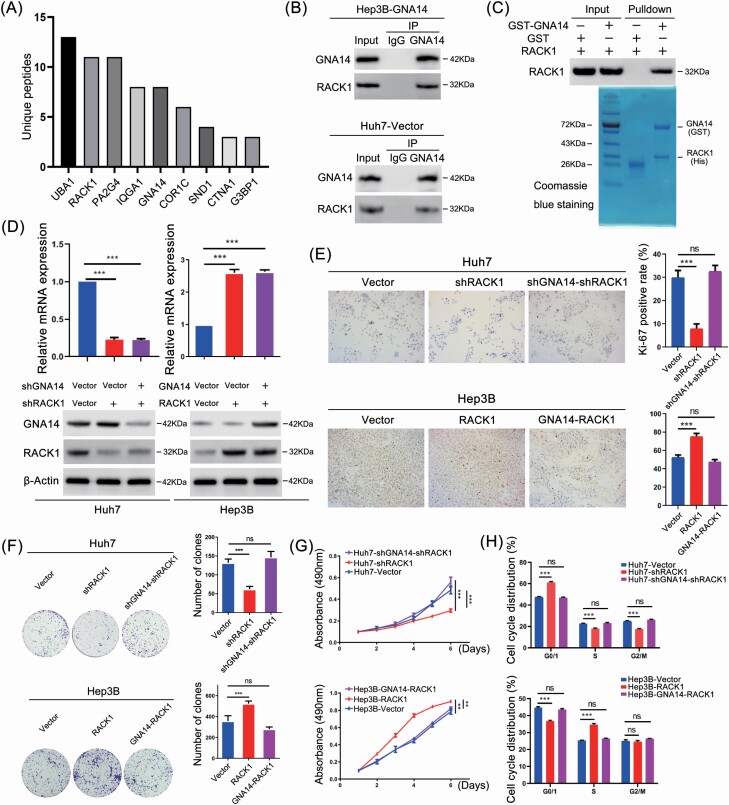
Figure 5.
GNA14 inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells through interacting with RACK1. (A) Hep3B-GNA14 cells were lysed and incubated with anti-GNA14 antibody followed by mass spectrometry. The histograms showed the Unique Peptides of each protenin identified except cytoskeleton-associated proteins and nutrient metabolism proteins. (B) Hep3B-GNA14 and Huh7 cell were lysed and incubated with anti-GNA14 antibody followed by western blot assay with anti-RACK1 antibody and IgG as negative control. (C) GST and GST-tagged GNA14 were purified with glutathione agarose beads and incubated with His-RACK1. The membranes were detected with anti-RACK1 antibody. GST and the purified lysate were indicated in Coomassie Blue staining. (D) The protein level of GNA14 and RACK1 was determined by western blot respectively in GNA14/RACK1-intervened Huh7 and Hep3B cell lines. (E) Representative images of Ki67 staining in RACK1- and GNA14-intervened Huh7 and Hep3B cell lines were shown. The histograms showed the percent of Ki-67 positive rate in each cell lines respectively. (F) The proliferation ability of RACK1- and GNA14-intervened Huh7 and Hep3B cell lines was monitored by colony formation assay, MTT assay (G) and cell-cycle analysis, DNA was stained by Propidium iodide (H). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 based on the Student’s t-test. Error bars, standard deviation.