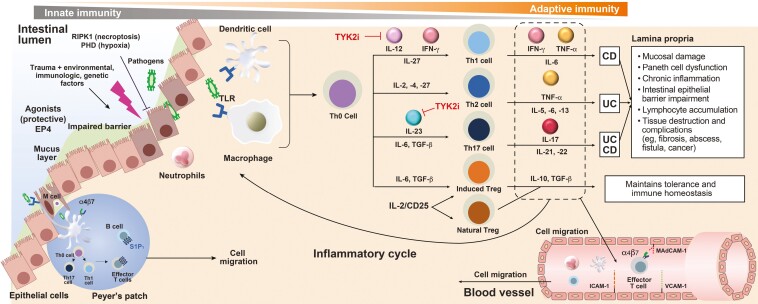
Figure 2.
IBD pathogenesis.3-9 Dysregulation of the mucosal immune response is a key trigger of IBD. The altered immune response is mediated through the activation of dendritic cells, which induces effector T cells, leading to an increase in the number of B cells and antibody production and an increase in the generation of proinflammatory signaling mediators such as IL-12, IL-23, IFN-gamma, IL-6, and TGF-β. TYK2 inhibitors disrupt dysregulated immune response by inhibiting IL-12, IL-23, and IFN-gamma inflammatory signaling. ILC indicates innate lymphoid cell; TGF, transforming growth factor; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.