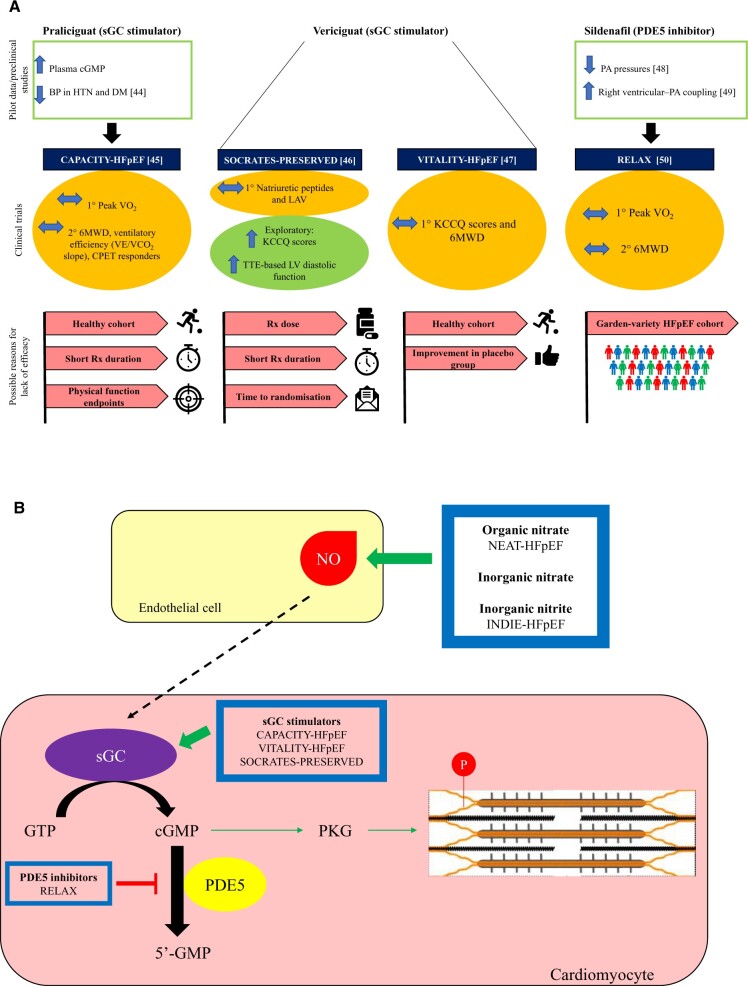
Figure 4.
Results of therapeutic trials targeting the nitric oxide–cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate–protein kinase G pathway. (A) Summarizes the pilot data (or pre-clinical data), clinical trial data and the potential reasons for neutral outcomes, whilst (B) highlights the specific intracellular pathways that each of the novel agents act on. None of these trials met their primary endpoints. However, all of these trials are plagued by specific and generic trial design limitations. The treatment arm of CAPACITY-HFpEF and SOCRATES-PRESERVED trials lasted for only 12 weeks, which may not have been long enough to lead to sustained improvements in the study endpoints. The patient cohort recruited in the CAPACITY-HFpEF and VITALITY-HFpEF trials may represent a ‘healthier’ cohort that is not representative of the ‘real-world’ patient cohort. In the CAPACITY-HFpEF study, only 20% of patients had elevated filling pressures and a majority of patients had New York Heart Association II symptoms. Attenuation of cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate levels in patients with HFpEF is due to the loss of upstream nitric oxide rather than an excessive breakdown of cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate.31 It is, therefore, not unexpected that attempting to augment cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate by inhibiting its breakdown did not lead to clinically meaningful improvements in patients’ haemodynamics or exercise capacity in the RELAX trial. Furthermore, whilst the agents used in these trials target the nitric oxide–cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate–protein kinase G pathway, none of the trials directly studied physiological endpoints of impaired vascular function, such as peripheral or coronary endothelial function. Additionally, the physical functioning endpoints (6-min walk distance and change in peak VO2) may not be able to discriminate among effective therapies because patients with HFpEF usually suffer from multiple comorbidities and their impaired physical functioning may be multifactorial in nature. BP, blood pressure; cGMP, cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate; DM, diabetes mellitus; GTP, Guanosine Triphosphate; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; HTN, hypertension; KCCQ: Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire; LAV, left atrial volume; NO, nitric oxide; PA, pulmonary artery; PKG, protein kinase G; sGC, soluble Guanylate Cyclase; 6MWD, 6-min walk distance.