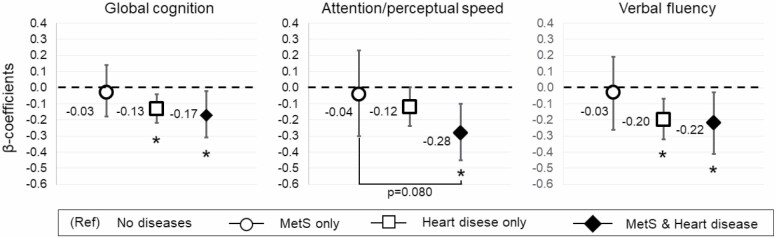
Figure 1.
Joint association of MetS and heart disease in relation to cognitive function. The figure shows the multiadjusted (by sex, education, physical activity, smoking, alcohol risk consumption, stroke/TIA, and APOE-ε4) β-coefficients estimated from 3 separate linear regression models for the association between MetS and heart disease in relation to global cognition, attention/perceptual speed, and verbal fluency. “MetS only” indicates the group who had MetS but no heart disease (n = 483), “Heart disease only” indicates the group who had heart disease but no MetS (n = 76), and “MetS and Heart disease” indicates the group with both diseases (n = 135). The reference group was “No disease” including people without MetS and without heart disease (n = 437). *p value < .05 (reference group = no diseases). APOE-ε4 = apolipoprotein E gene-ε4 allele; MetS = metabolic syndrome.