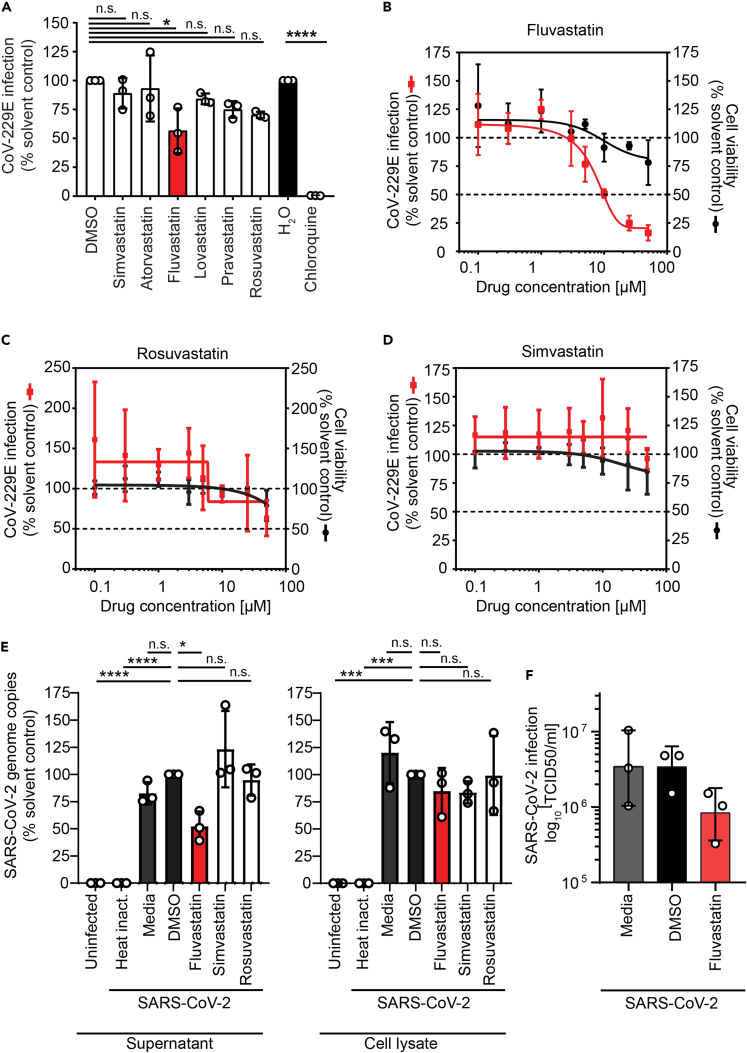
Figure 1.
Lipid-lowering drugs selectively reduce coronavirus infection in human cells
(A) Huh7.5 Fluc cells were pretreated 24 h with the indicated statins (5 μM) or chloroquine as positive control and then infected with HCoV-229E harboring a Renilla reporter gene (MOI 0.005) in the presence of the drugs. Renilla luciferase activity as a measure of infectivity was determined 48 h after infection. The HCoV-229E infectivity (Renilla luciferase activity) was normalized to cell viability measured by the constitutive expression of Firefly luciferase in Huh7.5 Fluc cells.
(B–D) Dose-response curves for the antiviral and cytotoxic effect of fluvastatin (B), rosuvastatin (C), and simvastatin (D) in Huh7.5 Fluc cells. Infection and statin treatment was performed as in (A) at the indicated statin concentration. The dotted lines indicate 100% and 50% infection and viablity.
(E) Fluvastatin decreases SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility of human respiratory epithelial Calu-3 cells. Virus genome copy numbers in cell lysates and supernatants from cells pretreated with selected statins (10 μM) or DMSO solvent control and infected with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI 2.0x10−5) are shown. Results are normalized to viral copy numbers in DMSO-treated cells.
(F) Number of infectious SARS-CoV-2 particles in cell culture supernatant from fluvastatin pretreated and SARS-CoV-2-infected Calu-3 cells (as in E) was determined by titration on Vero cells. (A–F) Mean ± SD of three independent biological replicates shown. One-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.0005, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.