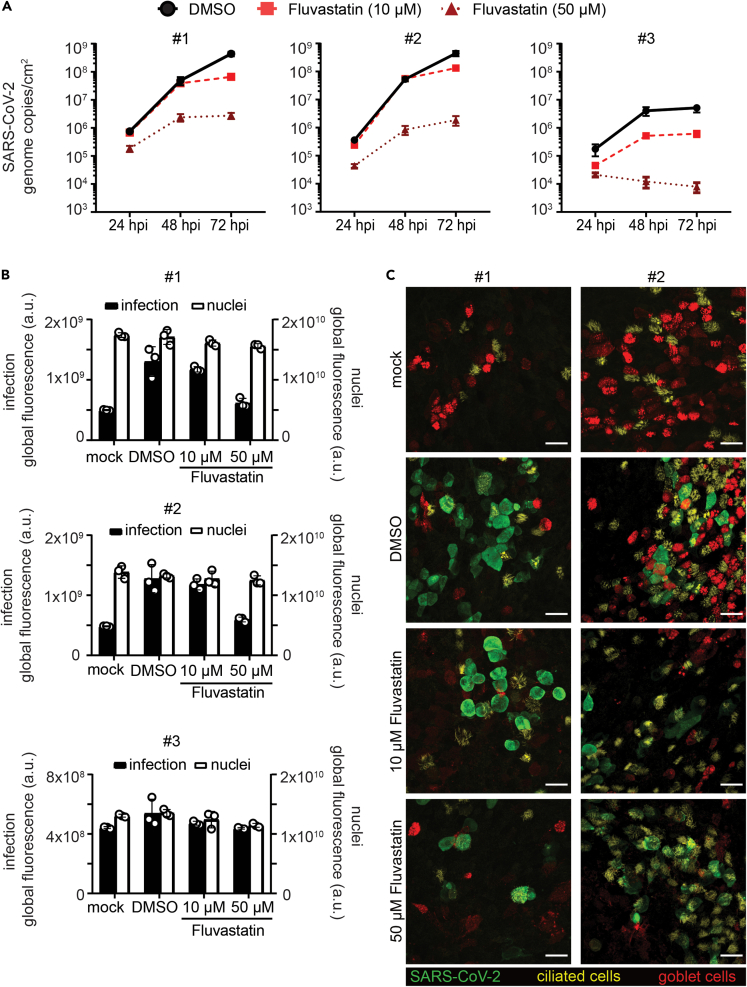
Figure 2.
Fluvastatin treatment reduces SARS-CoV-2 infection in HBEC ALI cultures
(A–C) HBEC ALI cultures from three donors were pretreated with DMSO solvent control or fluvastatin (10 μM or 50 μM) in the basal media for 24 h prior to SARS-CoV-2 infection at the apical side (4.5 × 104 PFU). (A) To assess viral replication, apical samples from HBEC ALI cultures were collected 24, 48, and 72 h postinfection by a 1-h wash in 300 μL growth medium. Progeny virus released within these 24 h periods were quantified by real-time q-PCR alongside an RNA standard. RNA genomes per ALI area in DMSO-treated samples (circle, black solid line) was plotted against time for the different statin concentrations (10 μM: square, red dashed line; 50 μM: triangle, dark red dotted line). Real-time q-PCRs were run in duplicates from three HBEC ALI inserts per sample. Data shown as mean of three biological replicates ± SEM. (B) ALI cultures were fixed at 72 h (endpoint) and stained for SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and nuclei and analyzed by immunofluorescence. Global fluorescence intensity of infection (black bars) and nuclei (white bars) was quantified from a fixed ROI omitting the well borders. Depicted are averages and SD in global fluorescence in arbitrary units from triplicates per condition from HBEC ALIs for each donor. (C) ALI samples at 72 h (endpoint) were stained for SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein for infection (green), mucin5AC for secretory cells (red) and acetylated tubulin for ciliated cells (yellow) and imaged on a scanning confocal microscope. Depicted are maximum intensity projections from z-stacks of representative sites for the different conditions from two different individuals. Scale bars, 25 μm.